Figure 3.
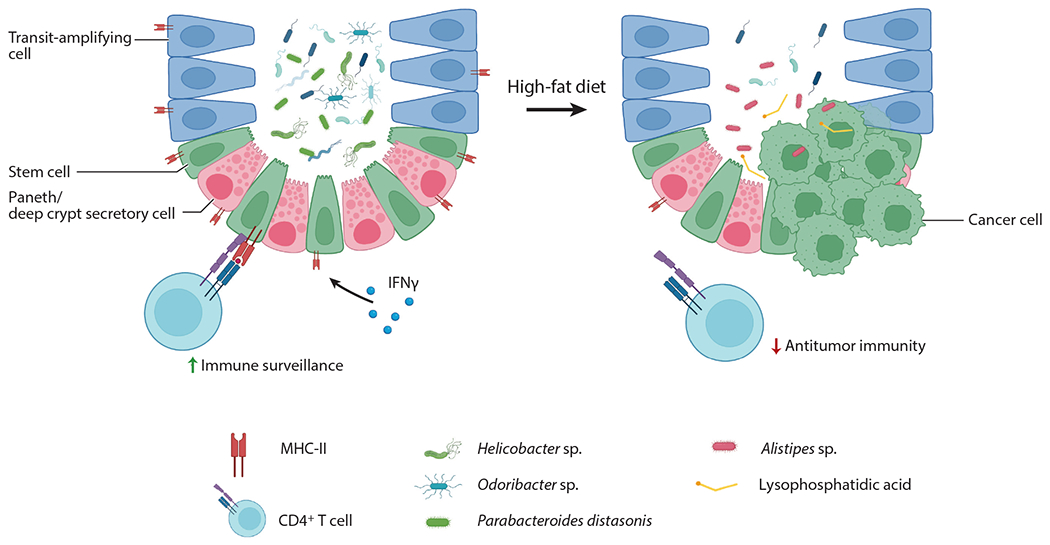
An HFD promotes CRC tumorigenesis through intestinal dysbiosis and decreased tumor immune surveillance. Beyaz et al. (32) found that an HFD reduces microbial diversity, particularly Helicobacter sp. and Odoribacter sp., leading to a decrease in MHC-II expression on intestinal epithelial cells and a reduction in antitumor immunity. Yang et al. (98) reported that an HFD promotes tumorigenesis through a shift in protective Parabacteroides distasonis to Alistipes sp. and an increase in the concentration of the protumorigenic fatty acid, lysophosphatidic acid. Figure adapted from images created with BioRender.com. Abbreviations: CRC, colorectal cancer; HFD, high-fat diet; IFN, interferon; MHC-II, major histocompatibility complex class II.
