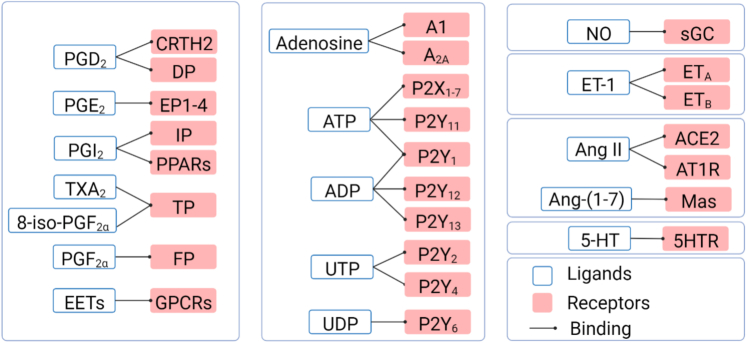
Figure 1.
Endothelium-Derived Factors and Their Receptors
The regulatory effect of endothelium-derived relaxing factors (EDRFs) and endothelium-derived contracting factors (EDCFs) on vascular tension depends on their specific receptor pathways. 5-HT = 5-hydroxytryptamine; 5HTR = 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor; 8-iso-PGF2α = 8-iso-prostaglandin F2α; A1, A2A = type 1 purinergic receptors; ACE2 = angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; ADP = adenosine diphosphate; Ang = angiotensin; AT1R = angiotensin type 1 receptor; ATP = adenosine triphosphate; CRTH2 = prostaglandin D2 receptor 2; DP = prostaglandin D2 receptor; EET = epoxyeicosatrienoic acid; EP = prostaglandin E receptor; ET = endothelin; ETA = endothelin receptor A; ETB = endothelin receptor B; FP = prostaglandin F2α receptor; GPCR = G protein–coupled receptor; IP = prostaglandin I2 receptor; Mas = Mas receptor; P2X = type 2X purinergic receptor; P2Y = type 2Y purinergic receptor; PG = prostaglandin; sGC = soluble guanylate cyclase; TP = thromboxane A2 receptor; TXA2 = thromboxane A2; UDP = uridine diphosphate; UTP = uridine triphosphate.