Figure 3.
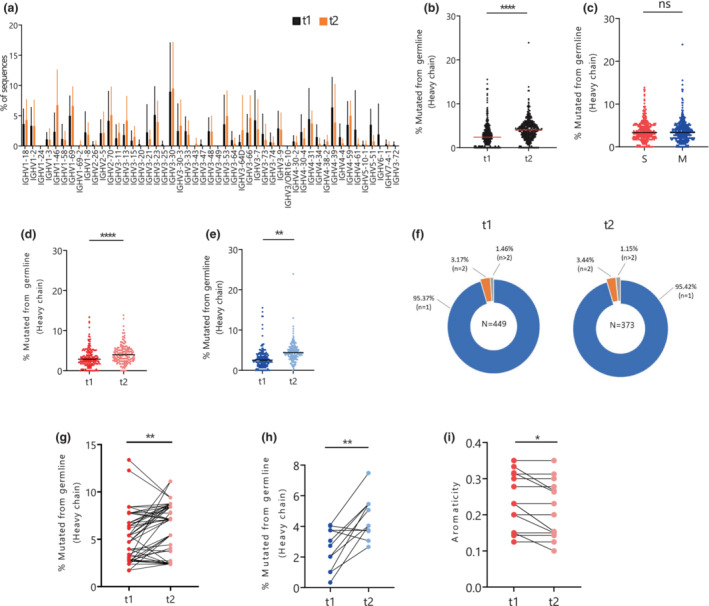
Maturation of receptor‐binding domain (RBD)–specific memory B cells over time. (a) Frequency of gene usage, as a percentage, of heavy chains across seven patients at t1 and t2. (b) Percentage mutated from germline in IgD− heavy chain across t1 and t2 in both severe (S; n = 3: 289036, 247004, 250002) and moderate (M; n = 4: 250011, 213007, 250017 and 213021) groups. (c) Percentage mutated from germline in IgD− heavy chain in the S and M group in both time points combined and (d) between t1 and t2 in the S and (e) M groups. (f) Percentage of clonal B cell receptor (BCR) population (singlets, n = 1; double, n = 2; more than two BCRs in a clone, n > 2) at t1 and t2 across seven individuals infected with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‐CoV‐2). (g) Increase in the percentage mutated from germline in heavy chain over time clones of the S and (h) M groups of individuals infected with SARS‐CoV‐2. (i) Decrease in aromaticity of CDR3H sequences from t1 to t2 over time clones of the S group. Statistical differences across disease severity were calculated using the two‐tailed unpaired t‐test (Mann–Whitney U‐test), with adjusted P‐values as *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001, ns, nonsignificant. The red horizontal line depicts median at that stage of disease. Nonparametric paired t‐test (Wilcoxon) was performed for statistical significance analysis for testing change in percentage mutation from germline and aromaticity in paired over time clones. Ig, immunoglobulin.
