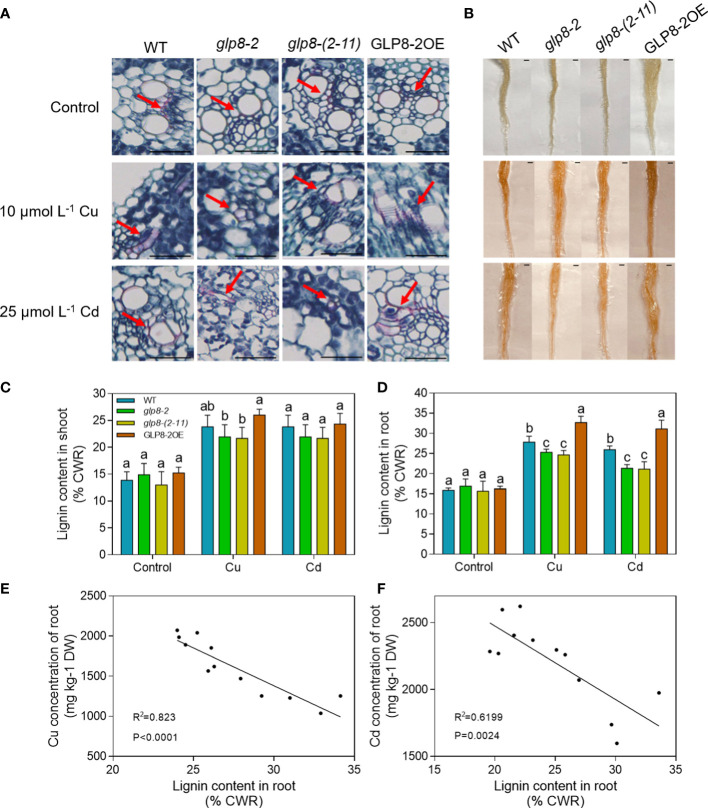
Figure 5.
OsGLPs involved in lignin accumulation in rice. (A) Effects of Cu or Cd stress on lignin deposition in WT (wild type) and transgenic rice. Seedlings grew for 5 days under normal conditions, 10 μmol L−1 CuSO4 treatment, or 25 μmol L−1 CdCl2 treatment. The stems of the rice plants were stained with Safranin O-Fast Green, paraffin embedded, and sectioned. The magnification was 400×. Red indicates that the lignin was successfully dyed. (B) Histochemical localisation of lignin in primary roots of two-week-old seedlings grown for 5 days under normal conditions, 10 μmol L−1 CuSO4 treatment, or 25 μmol L−1 CdCl2 treatment. The roots were stained with phloroglucinol solution, sliced, and placed on a stereo microscope to take pictures. Scale bar = 1 cm. (C, D) The lignin content in the root and shoot cell walls of two-week-old seedlings grown for 5 days under normal conditions, 10 μmol L−1 CuSO4 treatment, or 25 μmol L−1 CdCl2 treatment. (E, F) Correlation between root Cu/Cd content in rice and lignin content in the root cell walls of rice. These seedlings were treated with 10 μmol L−1 CuSO4 or 25 μmol L−1 CdCl2 for 5 days. Values are the mean ± SD; n = 3. Different letters indicate a difference of p ≤ 0.05 using the LSD test.