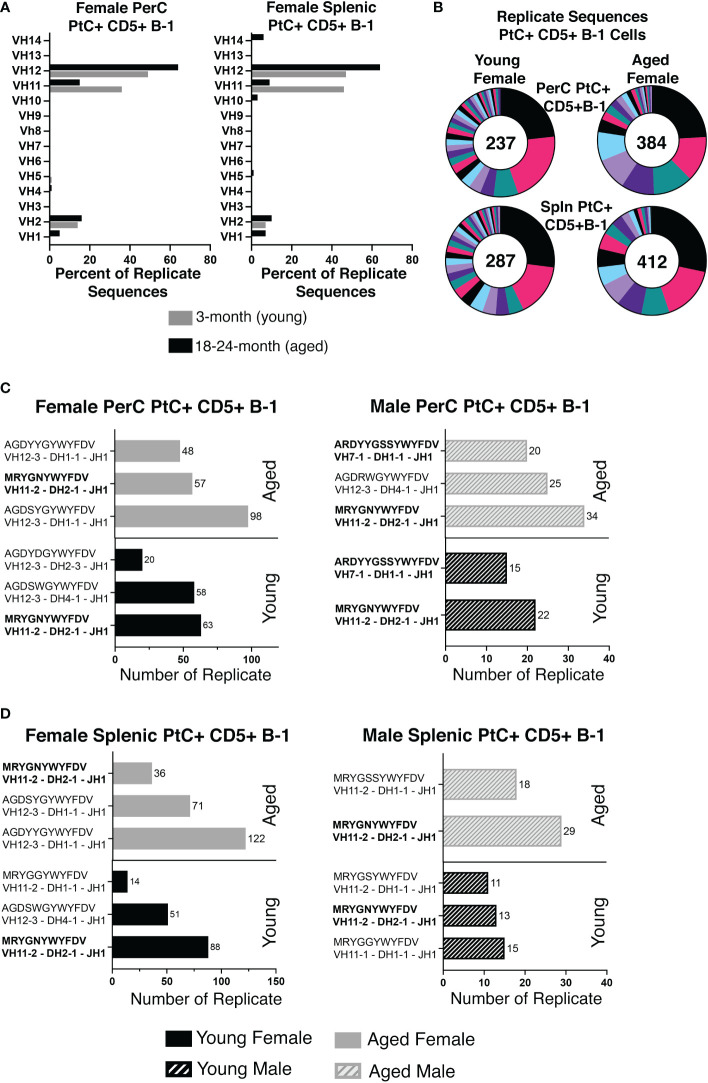
Figure 3.
Significant differences in female versus male peritoneal and splenic PtC+CD5+ B-1 cell CDR-H3 use. PtC+CD5+ B-1 cells were single-cell sorted from the peritoneal cavity or spleen of young and aged female BALB/c-ByJ mice (as presented in Figure 2 ). (A) The percent of VH gene segment usage within the replicate sequences. (B) Distribution of replicate CDR-H3 sequences in the young and aged (number in the middle represents the number of replicates within the population). Each color represents a unique CDR-H3 amino acid sequence. (C, D) For direct comparison of females and males, previously published (24) CDR-H3 analysis of young and aged malePtC+CD5+ B-1 cells is included. (C) Comparison of the most frequently utilized CDR-H3 sequences of peritoneal PtC+CD5+ B-1 cells from young and aged male and female mice. (D) Comparison of the most frequently utilized CDR-H3 sequences of splenic PtC+CD5+ B-1 cells from young and aged male and female mice. Results are based on 4 independent experiments with sequences combined from each independent experiment (n=11 for 3-month-old mice, n=15 for 23-26-month-old female mice). Statistics used: 2x2 chi-square tests.