Fig. 5.
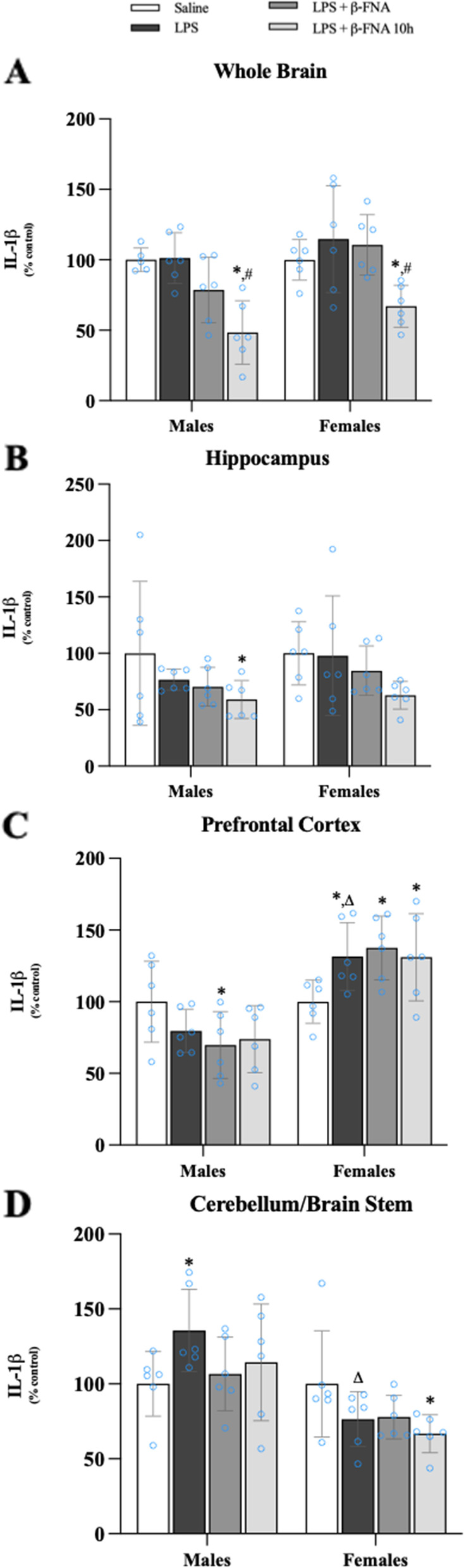
β-FNAs effect on LPS-induced IL-1β expression in the whole brain and brain regions (hippocampus, prefrontal cortex, and cerebellum/brain stem) of male and female C57BL/6J mice. Mice (n = 5–6/group) were injected (i.p.) with saline (control), LPS (0.83 mg/kg), LPS followed immediately by β-FNA treatment (50 mg/kg; i.p.; LPS + β-FNA), or LPS followed by β-FNA 10 h post-LPS (LPS + β-FNA 10 h). 24 h post-LPS, mice were terminated followed by tissue collection. Levels of IL-1β of whole brain (A), hippocampus (B), prefrontal cortex (C), and cerebellum/brain stem (D) of tissue homogenates were measured by ELISA. Data are reported as mean ± SEM. Two-way ANOVA indicated significant main effects of treatment (p < 0.001) and sex (p < 0.02) on IL-1β levels in the whole brain, but no significant effect of interaction (p = 0.39). Two-way ANOVA determined IL-1β in the hippocampus had a significant main effect of treatment (p < 0.05), but not sex (p = 0.32) or interaction (p = 0.86). In the prefrontal cortex two-way ANOVA determined IL-1β had a significant main effect of sex (p < 0.0001) and interaction (p < 0.01) but not treatment (p = 0.95). Two-way ANOVA determined in the cerebellum/brain stem that IL-1β had a significant main effect of sex (p < 0.001) and interaction (p = 0.04), but not treatment (p = 0.43). Pairwise comparisons were assessed using a Fisher’s LSD test; * indicates p < 0.05 vs. saline group; # indicates p < 0.05 vs. LPS group; Δ indicates p < 0.05 vs. males LPS
