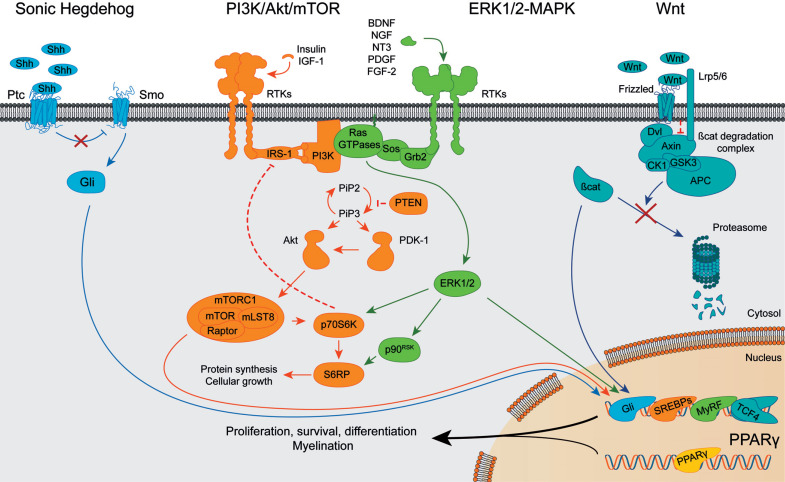
Fig. (2).
Schematic diagram of Shh, PI3K/Akt/mTOR, ERK1/2-MAPK, Wnt/β-catenin and PPARγ signaling pathways. Key elements of each pathway are shown when each route is active. Arrowheads indicate positive interactions while bars show inhibitory signals. Abbreviations: Shh: Sonic Hedgehog, Ptc: Patched, Smo: Smoothened, Gli: Glioma-associated oncogene family. BDNF: brain-derived neurotrophic factor, NGF: nerve growth factor, NT3: neurotrophin 3, RTKs: receptors tyrosine kinase, IRS-1: insulin receptor substrate 1, PI3K: phosphoinositide-3 kinase, PIP2: phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-biphosphate, PIP3: phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-triphosphate, PTEN: phosphatase and tensin homolog, PDK-1: 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase, Akt: protein kinase B, mTOR: mammalian target of rapamycin, mLST8: target of rapamycin complex subunit LST8, Raptor: regulatory associated protein of mTOR, p70S6K: Ribosomal protein S6 kinase beta-1, S6RP: Ribosomal protein S6, SREBPs: Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins. PDGF: platelet-derived growth factor, FGF-2: fibroblast growth factor 2, Grb2: growth factor receptor-bound protein 2, Sos: son of sevenless, ERK1/2: extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2, p90RSK: p90 ribosomal S6 kinase, MyRF: Myelin Regulatory Factor. Lrp5/6: Lipoprotein receptor-related proteins 5/6, Dvl: disheveled, GSK3: glycogen synthase kinase 3, CK1: casein kinase 1, APC: adenomatous polyposis coli, β-cat: β-catenin, TCF4: transcription factor 4. PPARγ: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ.