FIG 3.
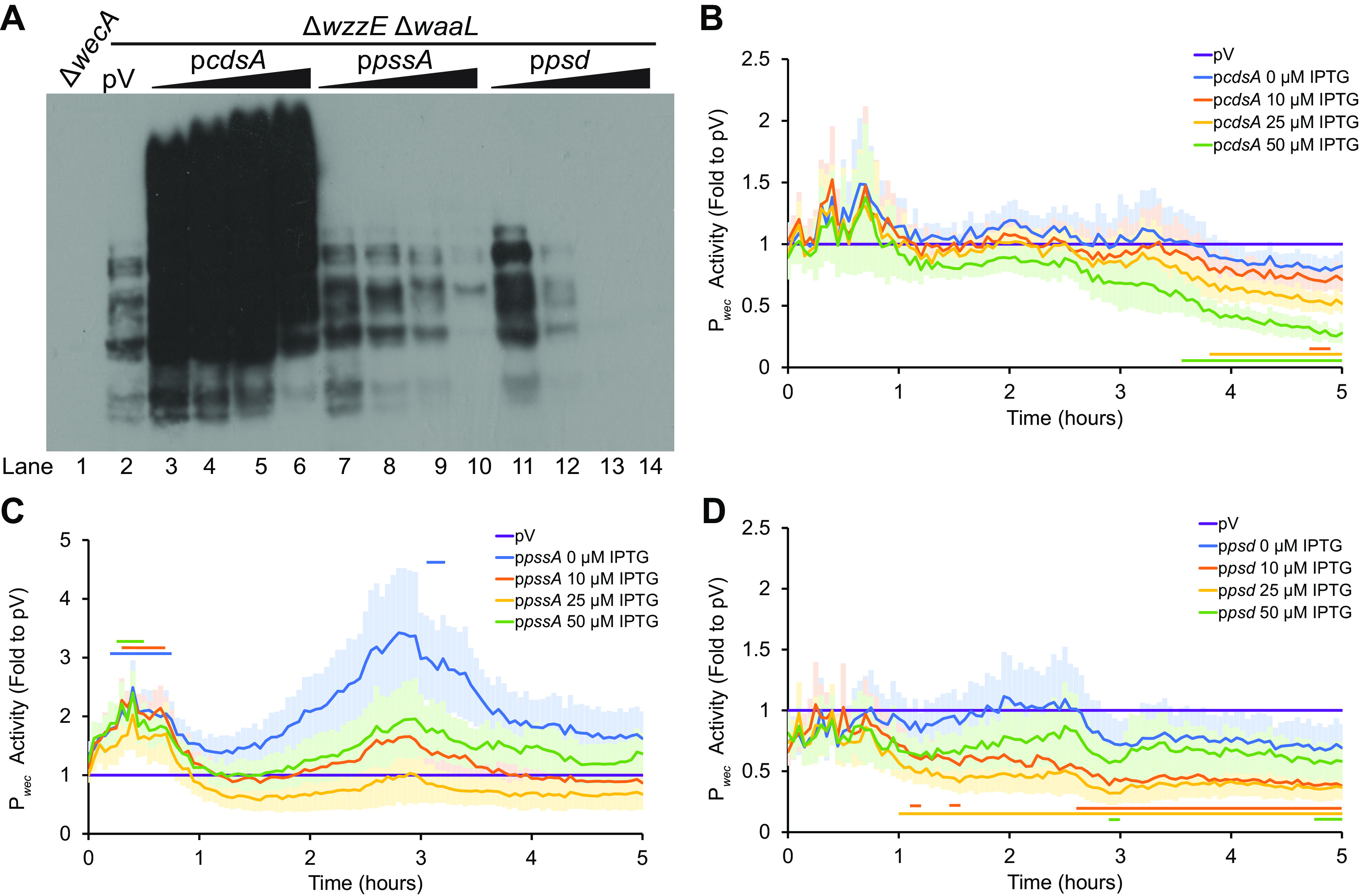
A phospholipid is the substrate for ECAPG synthesis. (A) The levels of ECAPG were assayed by immunoblotting in a strain that produces only ECAPG and not the other two forms of ECA (ΔwzzE ΔwaaL). The vector control (pV) treated with 50 μM IPTG is compared to strains overexpressing the indicated genes in phospholipid biosynthesis with increasing concentrations of IPTG (0, 10, 25, and 50 μM). A strain with a deletion of wecA, the first gene in the ECA biosynthesis pathway, serves as a negative control. Overexpression of cdsA causes large increases in the amounts of ECAPG, while overexpression of pssA and psd decrease ECAPG levels. Image is representative of three independent experiments. (B to D) Strains overexpressing genes in phospholipid biosynthesis and carrying a luciferase reporter for wec operon promoter (Pwec) activity were assayed for luminescence and OD600. The data are shown as fold value of the relative luminescence to the vector control and are means from six biological replicates ± the SEM. The empty vector (pV) sample contained the empty vector for phospholipid gene overexpression and the Pwec reporter and was treated with 50 μM IPTG. Horizontal bars: P < 0.05 by t test consistently for three or more time points. (B) Strains overexpressing cdsA have very similar Pwec activity to that of the empty vector control, with a decrease later in growth. (C) Strains overexpressing pssA have some increase in Pwec activity. (D) Overexpression of psd decreases Pwec activity.
