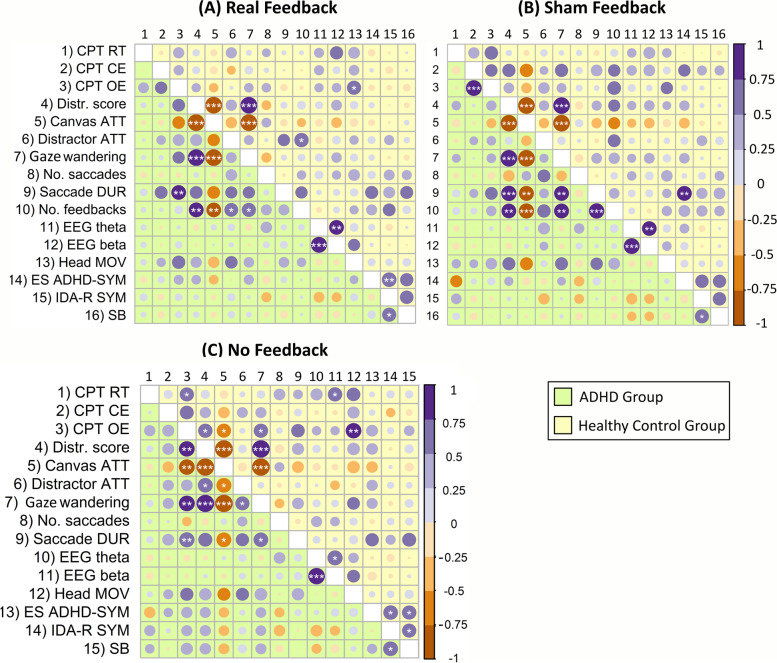
Fig. 5.
Exploratory correlation analysis. Correlation matrices including indications of statistical significance based on Benjamini–Hochberg corrected p-values are separately reported for both groups, the ADHD group (left of and below the diagonal) and HC (right of and above the diagonal). Correlations were calculated separately for the (A) real feedback, (B) sham feedback and (C) no feedback condition. Accordingly, correlations with the number of triggered feedback are not presented for the latter condition. The color coding of the strength of the Pearson correlations is shown on the right. Higher contrasts and greater circle seizes indicate stronger correlations. Abbreviations: Canvas ATT: Time of task focus indicated by attended canvas dwell times, CE: Commission errors, CPT: Continuous performance task, Distractor ATT: Attended distractors percentage dwell times, Distr. Score: Distractibility score, ES ADHD-SYM: Experience sampling self-rated ADHD symptoms, Head MOV: Head movements, IDA-R SYM: ADHD symptoms observer-rated via the IDA-R, No. feedbacks: Total number of feedback triggered, No. saccades: Total number of saccades, OE: Omission errors, RT: Reaction times, Saccade DUR: Average saccade durations, SB: ADHD symptoms self-rated via the ADHS-SB. *p < .05, **p < .01, ***p < .001