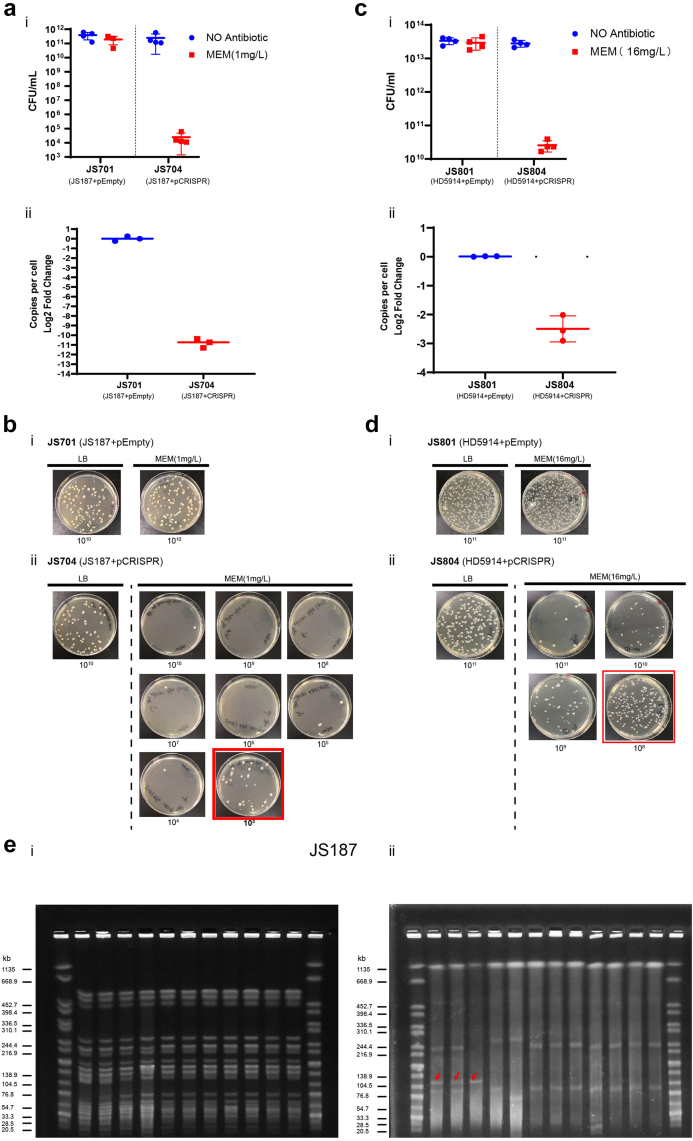
Fig. 4.
Killing efficiency of IncFII plasmids by native CRISPR. Plasmid curing of JS187 (blaKPC, MEM-resistant) (ai, b) and HD5914 (blaKPC, MEM-resistant) (ci, d) with pEmpty (negative control) or pCRISPR. The plasmid killing efficiency was calculated by the reduced MEM-resistant colonies (LB with MEM) in total cell counts (LB with no antibiotic) (n = 4). CFU, colony-forming units. p187-2 plasmid (IncFII-blaKPC plasmid) copy number (aii) and pHD5914 plasmid (IncFII-blaKPC plasmid) copy number (cii) determined by quantitative PCR in either JS701/JS801(JS187/HD5914 harbouring pEmpty plasmid) or JS704/JS804 (JS187/HD5914 harbouring pCRISPR plasmid). (e) XbaI (i)and S1 (ii) PFGE of genomic DNA of JS187 and its derivatives. Marker: XbaI-digested DNA of Salmonella Braenderup H9812. The red arrows in S1-PFGE (ii) represent the p187-2 plasmid (129,684 bp, CP025468.1). JS704: JS187 harbouring pCRISPR; JS531: E. coli Top 10 harbouring p187-2 plasmid. JS708, JS709, JS800, and JS805-JS900: p187-2 cured JS187. Two examples of potential recombination events associated with p187-2 curing are found in JS708 and JS709 and a larger size of p187-1 plasmid (246,557 bp, CP025467.1) and p187-4 plasmid (106,402 bp, CP025470.1).