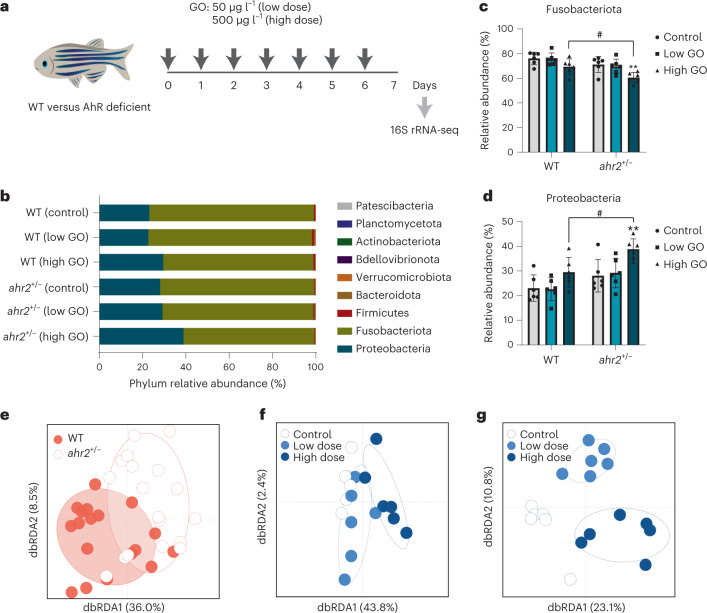
Fig. 1. AhR-dependent changes in the gut microbiome of adult zebrafish.
a, Experimental design for the seven-day exposure regimen in adult zebrafish (WT and ahr2+/−). b, The most abundant bacteria phyla of the gut microbiota among genotypes and treatments. Each bar represents the average of six individuals in each condition. c,d, Relative phylum abundance of Fusobacteriota (c) and Proteobacteria (d) in WT versus ahr2+/− fish exposed to GO. The error bars represent the mean values ± s.d. of six individuals. Significant differences between the treatments and genotypes are shown. Two-way analysis of variance using Tukey’s multiple comparisons test was used to analyse the statistical differences (Fusobacteriota, **p = 0.0065, #p = 0.0265; Proteobacteria, **p = 0.0055, #p = 0.0186). e, Supervised analyses of the microbiota composition between the two genotypes. f,g, Impact of GO on gut microbiota composition among WT (f) and ahr2+/− (g) zebrafish. dbRDA, distance-based redundancy analysis. Differential abundances of ASVs are shown in Supplementary Fig. 5. Credit: fish in a, Adobe Stock.