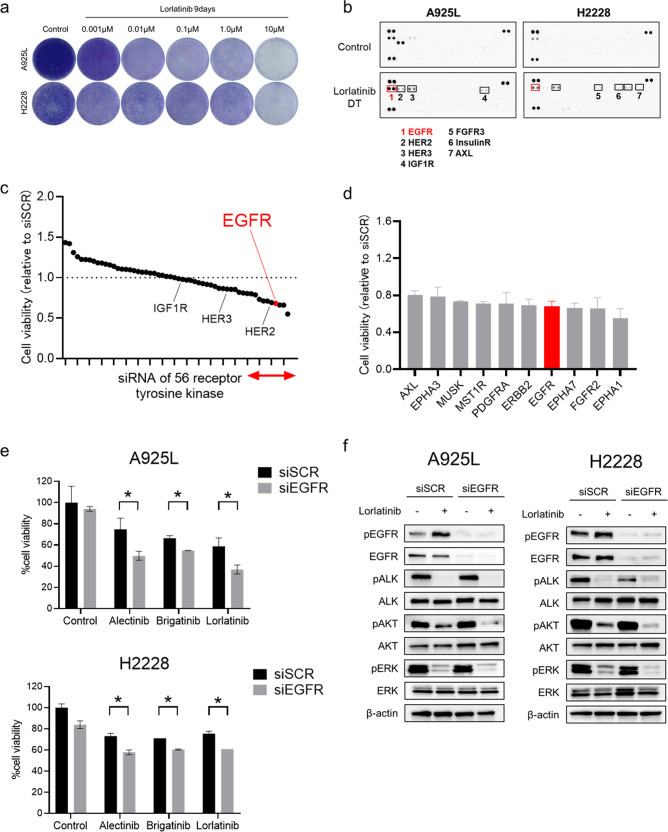
Fig. 1. EGFR signaling plays a pivotal role in the adaptive resistance of ALK-rearranged NSCLC cells.
a A925L and H2228 cells were visualized after crystal violet staining following 9 days of treatment with the indicated concentrations of lorlatinib. The drugs were replenished every 72 h. b Human phospho-RTK array analysis of parental cells and DT cells in A925L and H2228 cells. c, d Effect of a combination of lorlatinib (100 nmol/L) and knockdown of 56 receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) from the Silencer® Select human kinase siRNA library V4 on the viability of A925L cells was assessed using MTT assays. The 56 RTKs are rank-ordered from highest to lowest according to their inhibitory effect on the viability of A925L cells relative to nonspecific control siRNA. The effects of the top 10 genes indicated by a red line are further shown in d. e A925L and H2228 cells treated with nonspecific control siRNA or EGFR-specific siRNAs were incubated with or without alectinib (100 nmol/L), brigatinib (100 nmol/L), or lorlatinib (100 nmol/L) for 72 h and cell viability was detected using MTT assays. *P < 0.05 (one-way ANOVA). f Western blotting of A925L and H2228 cells treated with nonspecific control siRNA or EGFR-specific siRNA and incubated with or without lorlatinib (100 nmol/L) for 4 h. Data are represented as mean ± S.D.