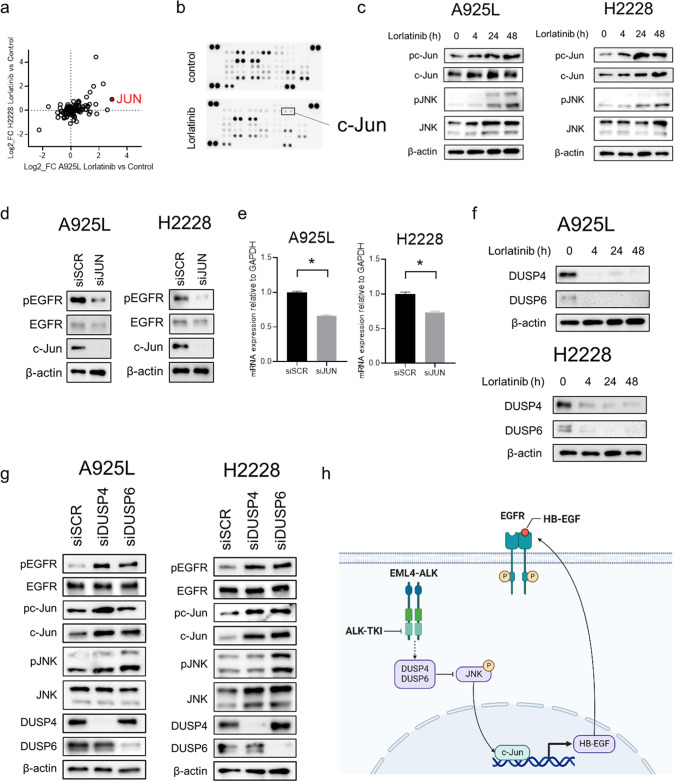
Fig. 3. EGFR activation is induced by JNK/c-Jun axis activation via suppression of DUSP4 and DUSP6.
a Scatterplot of genes in the KEGG_ERBB_SIGNALING_PATHWAY gene set in either A925L or H2228 DT cells vs. that in parent cells. b Human phospho-kinase array analysis of parental A925L and H2228 cells, as well as cells treated with lorlatinib (100 nmol/L) for 48 h. c Western blotting of A925L and H2228 cells treated with lorlatinib (100 nmol/L) for the indicated durations. d A925L and H2228 cells were incubated with nonspecific control siRNA or JUN-specific siRNA and lysed, and the indicated proteins were detected using western blotting. e qPCR of heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (HB-EGF) in parent A925L and H2228 cells and cells incubated with nonspecific control siRNA or JUN-specific siRNA. *P < 0.01 (unpaired t-tests). f Western blotting of A925L and H2228 cells treated with lorlatinib (100 nmol/L) for the indicated durations. g A925L and H2228 cells were incubated with nonspecific control siRNA and DUSP4 or DUSP6-specific siRNA and lysed, and the indicated proteins were detected using western blotting. h Schematic diagram showing the mechanisms of adaptive resistance, including activation of EGFR signaling via endogenous HB-EGF stimulation, the feedback loop of which was induced by the JNK/c-Jun axis, in ALK-rearranged NSCLC cells. Data are represented as mean ± S.D.