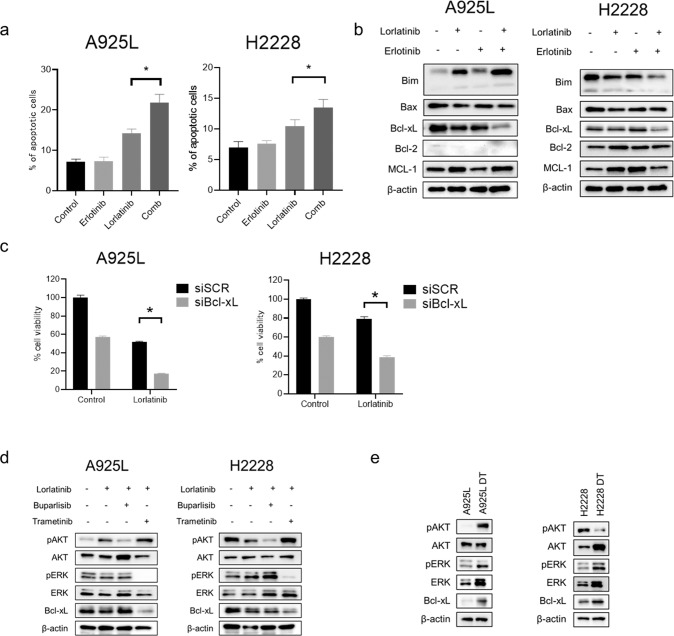
Fig. 5. Combination therapy with lorlatinib and erlotinib inhibits cell proliferation by inducing apoptosis via suppression of Bcl-xL.
a Apoptotic cell percentages of A925L and H2228 cells, which were double-stained with annexin V and propidium iodide, were detected using flow cytometry following treatment with lorlatinib (100 nmol/L), erlotinib (100 nmol/L), or a combination of lorlatinib and erlotinib for 48 h. *P < 0.05 (one-way ANOVA). b A925L and H2228 cells were incubated with lorlatinib (100 nmol/L), erlotinib (100 nmol/L), or a combination of lorlatinib and erlotinib for 96 h, and the indicated proteins were detected using western blotting. c A925L and H2228 cells treated with nonspecific control siRNA or Bcl-xL-specific siRNAs were incubated with or without lorlatinib (100 nmol/L) for 72 h. Cell growth was determined using MTT assays. *P < 0.01 (two-way ANOVA). d A925L and H2228 cells were incubated with lorlatinib (100 nmol/L), a combination of lorlatinib and buparlisib (100 nmol/L), or a combination of lorlatinib and trametinib (100 nM) for 96 h, and the indicated proteins were detected using western blotting. e Western blotting of parental cells and DT cells generated from A925L and H2228 cells. Data are represented as mean ± S.D.