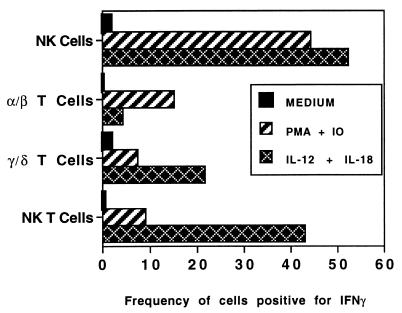
FIG. 5.
Production of IFN-γ is induced in NK, NK T, and γ/δ T cells by incubation with IL-12 and IL-18. Peritoneal cells were harvested from C57BL/6 mice 24 h after i.p. injection of 2 × 104 CFU of Listeria. Cells were incubated in medium alone or in PMA (10 ng/ml)–ionomycin (IO; 1 μM) for 3 h or with rIL-12 (5 ng/ml) and rIL-18 (50 ng/ml) for 18 h, with brefeldin A (10 μg/ml) added for the final 3 h of each condition. Cells were stained with FITC- or PE-conjugated antibodies to subset-specific surface markers and then fixed, permeabilized, and incubated with anti-IFN-γ-APC prior to analysis by flow cytometry. Frequencies of IFN-γ+ cells were calculated after gating on either NK1.1+ H57− (NK cell), NK1.1+ H57+ (NK T-cell), NK.1− H57+ (α/β T-cell), or CD3+ GL3+ (γ/δ T-cell) populations. Results are representative of three experiments. IFN-γ is also produced in these subsets of lymphocytes after incubation with IL-12 in combination with IL-1 and TNF-α (not shown). IFN-γ was not detectable in B cells under these conditions or in any population unless secretion was inhibited by brefeldin A.