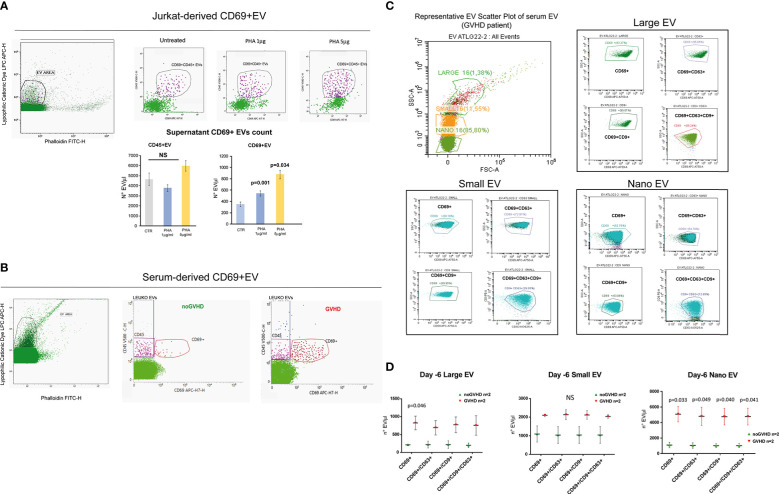
Figure 4.
Phenotypic characteristics of CD69+ EVs in HSCT samples. (A) Representative gating strategy for EV detection from un-stimulated CD69+ Jurkat T cells and upon stimulation with PHA (1 or 5 μg/ml) for 72 h. Bar graphs represent the concentration of CD69+ EVs and CD45+ EVs in the culture supernatants. (B) Representative gating strategy for EV detection in the serum of HSCT patients. (C) Cytoflex analysis of serum EV in a representative GVHD patient. Plots refer to the concentration of CD69+, CD69+CD63+, CD69+CD9+, CD63+CD9+CD63+ among large (900 µm), small (160–500 nm), and nano (100 nm) EV fraction (see Supplementary Figure 1 ). (D), Graphs charts of serum CD69+, CD69+CD63+, CD69+CD9+, CD63+CD9+CD63+ EVs according to size distribution in GVHD (n = 2) and noGVHD patients (n = 2). Values are expressed as number of EV/μl. Data are represented as mean +/- S.D. NS, Not Significant.