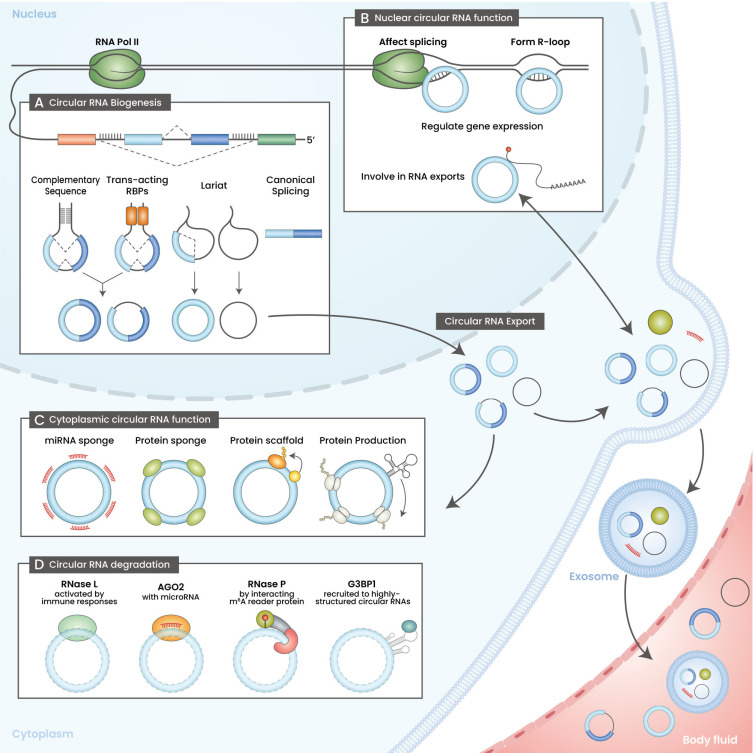
Fig. 1. The life cycle of circular RNA.
(A) Circular RNA biogenesis. Circular RNAs are produced through pre-mRNA back-splicing or by-products of splicing lariats. Back-splicing is facilitated by complementary sequences present in the flanking introns or trans-acting RBPs (RNA binding proteins). (B) Biological roles of nuclear circular RNAs. Circular RNAs can remain in the nucleus and function as gene expression regulators. Nuclear circular RNAs affect splicing by interacting with RNA polymerase II or forming R-loops with genomic DNA. Moreover, nuclear circular RNAs can modulate RNA export. (C) Biological roles of cytoplasmic circular RNAs. Most of the well-known functions of circular RNAs are cytoplasmic (e.g., miRNA sponge, protein sponge, protein scaffold, and template for protein production). Moreover, circular RNAs can be packaged into exosomes and circulated throughout the body as a body fluid. (D) Circular RNA degradation. The known mechanisms accelerating circular RNA degradation have been illustrated.