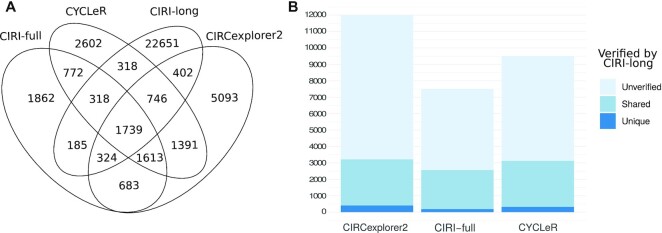
Figure 6.
Comparative study with CIRI-long data. (A, B) The results of the comparison between Illumina-based methods and a Nanopore-based method. (A) shows a Venn diagram of the length adjusted (<2000) set of assembled transcripts for each tool. (B) A bar graph representation of the same data, but with emphasis on overlapping regions from the Venn diagram. In (B), the assembled transcripts for each Illumina-based tool are divided into verified (by CIRI-long) or unverified. The latter are further subdivided into unique—the transcripts that are shared only by one Illumina-based tool and CIRI-long, and shared—the transcripts that are shared by two or more Illumina-based tools and CIRI-long. CIRI-full has the lowest transcript count in every category. This is due to the length limit of its underlying assembly based on the library insert size. When comparing CIRCexplorer2 and CYCLeR, we notice that CIRCexplorer2 has only ∼100 more verified transcripts, while simultaneously having ∼3000 more unverified transcripts. Based on the information provided by the simulated benchmark, it is a safe assumption that the extra isoforms produces by CIRCexplorer2 are primarily erroneous assemblies.