Figure 1.
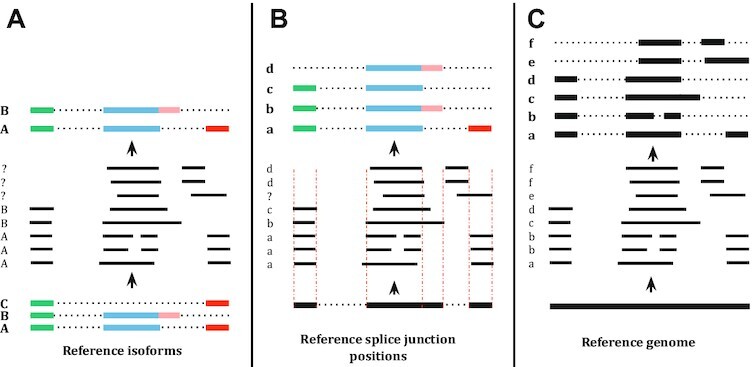
AS isoform detection tools can be put on a spectrum in terms of their reliance on reference annotations. (A) On the left of the spectrum, the tool is fully dependent on the known isoform annotations and is thus unable to discover any novel isoforms. Each read is annotated by the isoform that it best matches or is discarded if it does not match any isoform. (B) In the middle, the tool is partially reliant on the isoform annotation; novel isoforms can be detected as long as they are composed of known splice junctions (i.e. boundaries of known isoforms). The split-alignment boundary of each read is corrected to best matching splice junction position. If a read has a novel splice junction position, the tool will have difficulty identifying its isoform structure. (C) On the right, the tool does not rely on the reference annotation. Instead, it relies solely on the split alignment of the reads to the reference genome.
