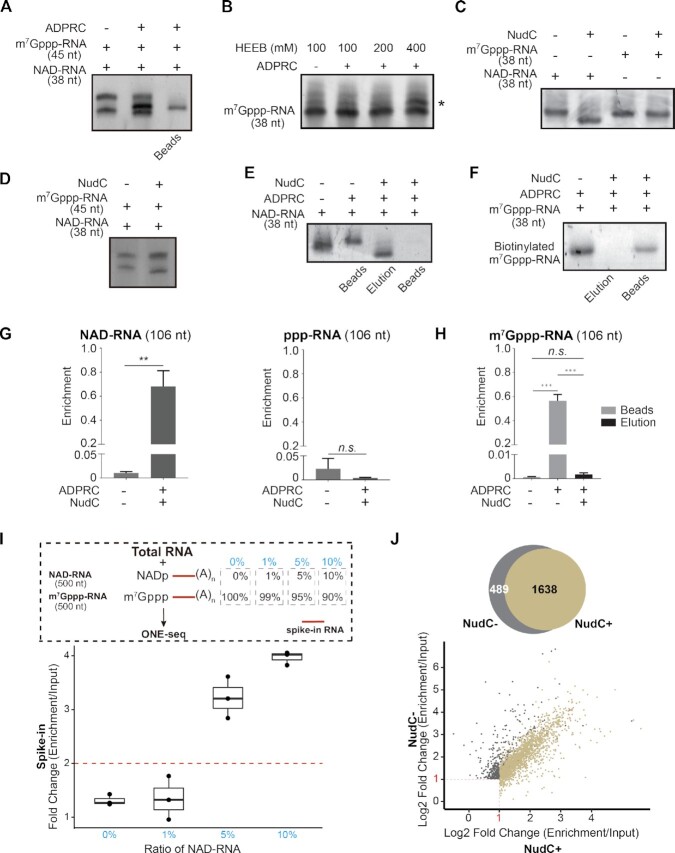
Figure 3.
The validation of ONE-seq. (A) HEEB reacts with NAD-RNA (38 nt), but not m7Gppp-RNA (45 nt), to yield a biotinylated form. (B) HEEB, only at high concentration (400 mM), reacts with m7G-capped RNA (38 nt), as evidenced by an upper band in the TBE-UREA gel (marked by asterisk). (C) NudC can de-cap NAD-RNA (38 nt), but not m7G-capped RNA (38 nt), as shown by a lower-sized band corresponding to the de-capped product in the TBE-UREA gel. (D) In the same reaction, NudC was able to selectively de-cap NAD-capped (38 nt) but not m7G-capped RNA (45 nt). (E) NudC-mediated de-capping elutes NAD-RNA (38 nt) from streptavidin beads. (F) NudC cannot elute biotinylated m7G-RNA (38 nt) from the streptavidin beads. (G) qRT-PCR analysis shows that NAD-RNA (106 nt), but not ppp-RNA (106 nt), can be enriched by ONE-seq. (H) qRT-PCR analysis shows that streptavidin beads bound HEEB-reacted m7G-capped RNA (106 nt) cannot be eluted by NudC (Two-tailed Student's t test: ***P < 0.001; **P < 0.01; n.s., not significant). (I) RNA-seq experiment of spike-in RNAs determines the sensitivity of ONE-seq. Top panel: schematic workflow of total RNAs and polyadenylated spike-in RNAs that had different ratios of NAD-RNA (500 nt). Two spike-in RNAs with identical sequence (500 nt) but have either NAD or m7G-cap, followed by polyA tails are used; bottom panel: fold change of normalized read counts from spike-in RNA between enrichment and input samples in different ratios of NAD-RNA. Total RNAs were from liver tissues of 18-month mice. The nominal ratios of NAD-RNA were highlighted in blue. (J) Epitranscriptome assessment of NudC to minimize the noise of m7G-RNAs. Two-fold enrichment of read counts was used as the cutoff. Standard ONE-seq identified 1,638 NAD-RNAs, while 489 false-positive NAD-RNAs were found without the use of NudC, presumably derived from m7G-capped RNAs. Total RNAs were from liver tissues of 12-month mice.