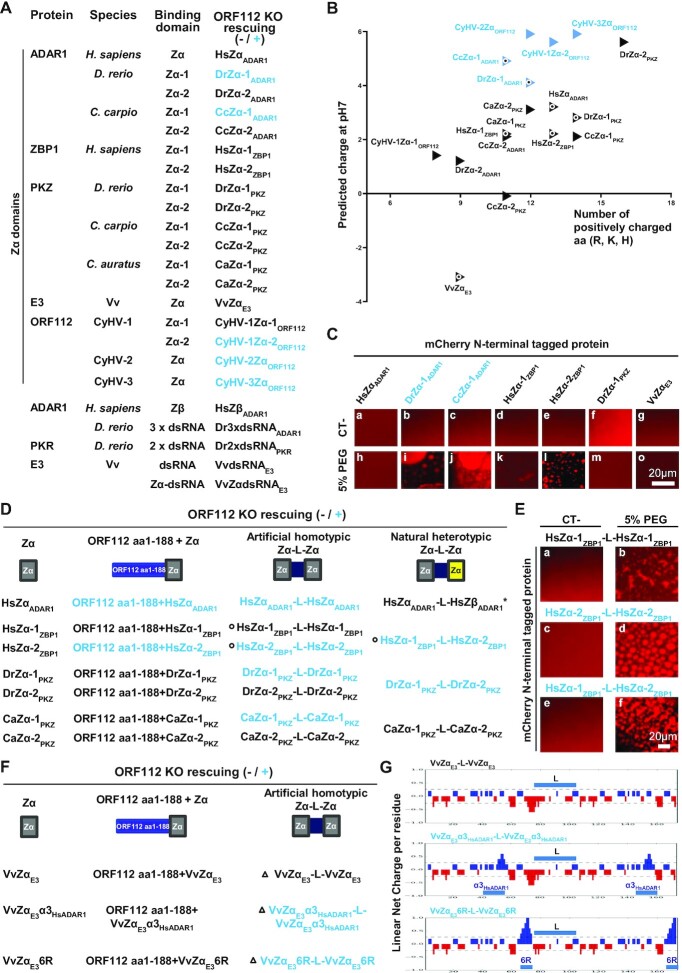
Figure 9.
Rescuing of CyHV-3 ORF112 KO requires the expression of a Zα domain-containing protein able to mediate both LLPS and B-to-Z transition. (A, D and F) The ability of Zα and dsRNA binding domains from various origins to rescue the lethal effect of ORF112 deletion on viral growth in cell culture was tested by transfection of the CyHV-3 BAC ORF112 KO plasmid into CCB cells together with a recombining fragment encoding the protein to be tested and ORF112 flanking regions, in order to induce homologous recombination at the ORF112 locus (sequences of the proteins tested are provided in Supplementary Table S2). At 6 days posttransfection, the cells were examined by epifluorescence microscopy (the BAC cassette encodes EGFP). Throughout this figure sequences able or not able to rescue virus replication are presented in blue or black, respectively. (B) Representation of global predicted charge versus the number of positively charged amino acids for the Zα domains listed in panel A. Black circles show the proteins selected for LLPS experiment presented in panel C (a version of this figure including Zα domains of mouse proteins is provided as supplemental material, Figure S4). (C) In vitro LLPS induced by incubation of the indicated mCherry N-terminal tagged Zα domains (10 μM) with PEG-6000 (5%, v/v). (D) Ability of selected Zα domains (left column) to rescue the lethal effect of ORF112 deletion on viral growth in cell culture when expressed in fusion to the N-terminal domain of CyHV-3 ORF112 (ORF112 aa1–188, second column), as artificial homotypic tandem Zα domains joined by a linker (third column) or as natural heterotypic tandem Zα domains (fourth column). The asterisk highlights that HsZβADAR1 does not have Z-DNA binding activity. Linker sequences were derived from the sequence of the protein from which the first Zα domain was derived. Black circles show the proteins selected for the LLPS experiment presented in panel E and performed as described in panel C. (F) Ability of VvZαE3 and derived mutant Zα domains (left column) to rescue the lethal effect of ORF112 deletion on viral growth in cell culture when expressed in fusion to the N-terminal domain of CyHV-3 ORF112 (ORF112 aa1–188, second column), and as artificial homotypic tandem Zα domains joined by a linker (sequence of the linker was derived from Hs ZBP1, third column). Black triangles show the proteins selected for net charge distribution analysis presented in panel G.