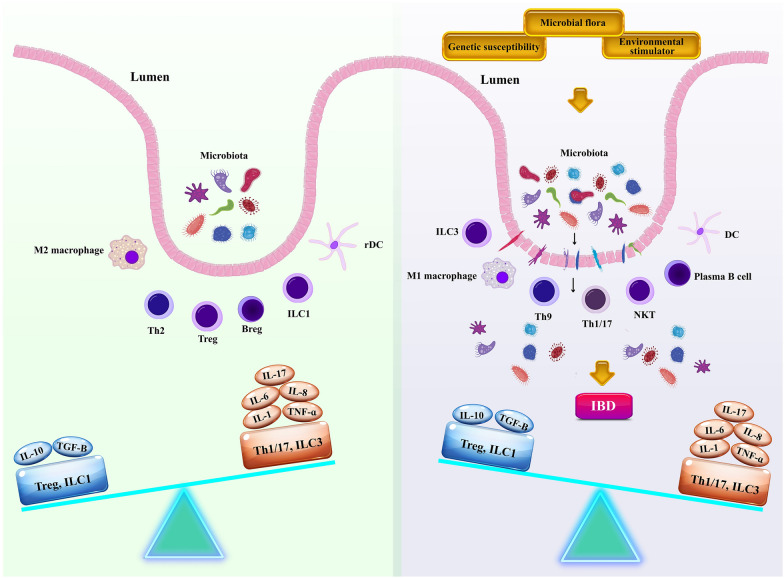
Fig. 1.
The IBD pathogenesis. The interactions between environmental factors, genetic susceptibility, and microbial flora may perturb intestinal hemostasis and thus induce the transduction of dysregulated immune responses and underlie resultant tissue damage. Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), innate lymphoid cells (ILC), T helper cell (Th), interleukin (IL), transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), regulatory B cells (Bregs), regulatory T cells (Tregs), regulatory dendritic cells (rDCs), natural killer T (NKT) cells, tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα)