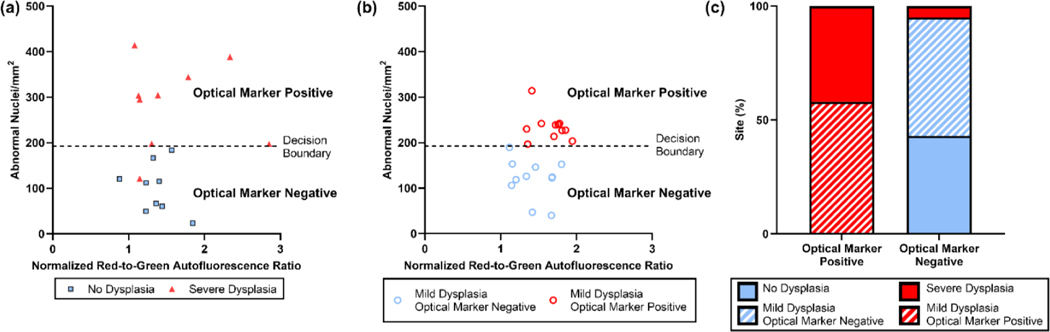
Fig. 2.
Characterization of sites based on optical markers. (a) Sites with no dysplasia had lower values of optical markers, while sites with severe dysplasia had higher values of optical markers. Nearest centroid classification was used to define a decision boundary between sites with no dysplasia and sites with severe dysplasia. (b) Sites with mild dysplasia were divided into two categories based on the decision boundary: optical marker negative or optical marker positive. (c) Sites that were optical marker negative included all sites with no dysplasia and only one site with severe dysplasia; sites that were optical marker positive included all but one site with severe dysplasia. Sites with mild dysplasia were roughly evenly distributed in the two groups.