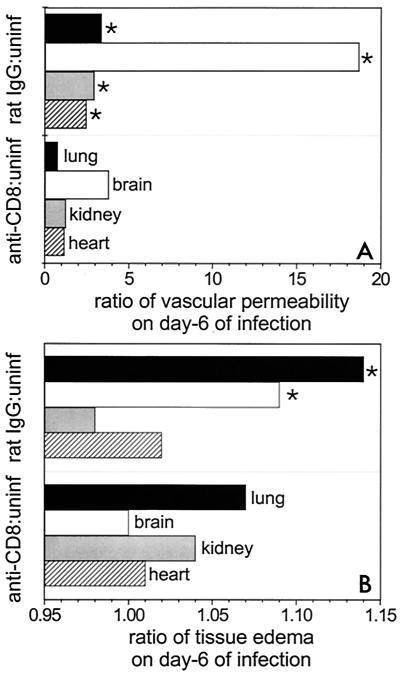
FIG. 4.
Ratios of vascular permeability (A) and tissue edema (B) in CD8+ T-cell-depleted mice (anti-CD8) infected with P. berghei malaria to vascular permeability and tissue edema in uninfected controls (uninf). These ratios are compared with the ratios of vascular permeability (A) and tissue edema (B) in rat IgG-treated and infected mice (rat IgG) to vascular permeability and tissue edema in uninfected controls. Vascular permeability was determined by the Evans Blue technique for selected tissues from groups of eight mice. The ratios of wet weight to dry weight for selected tissues were determined on day 6 of infection for groups of five mice. The vascular permeability or ratio of wet weight to dry weight for infected groups of animals (anti-CD8 mAb and rat IgG mAb treated) were divided by values for uninfected animals. Similar results were obtained in replicate experiments for vascular permeability and in duplicate experiments for tissue edema. An asterisk indicates statistical significance (P < 0.05) for a comparison of a group of infected CD8-depleted mice and infected rat IgG-treated controls.