Figure 5: Engineered AAVs can efficiently transduce cultured human brain microvascular endothelial cells, ex vivo macaque and human brain slices.
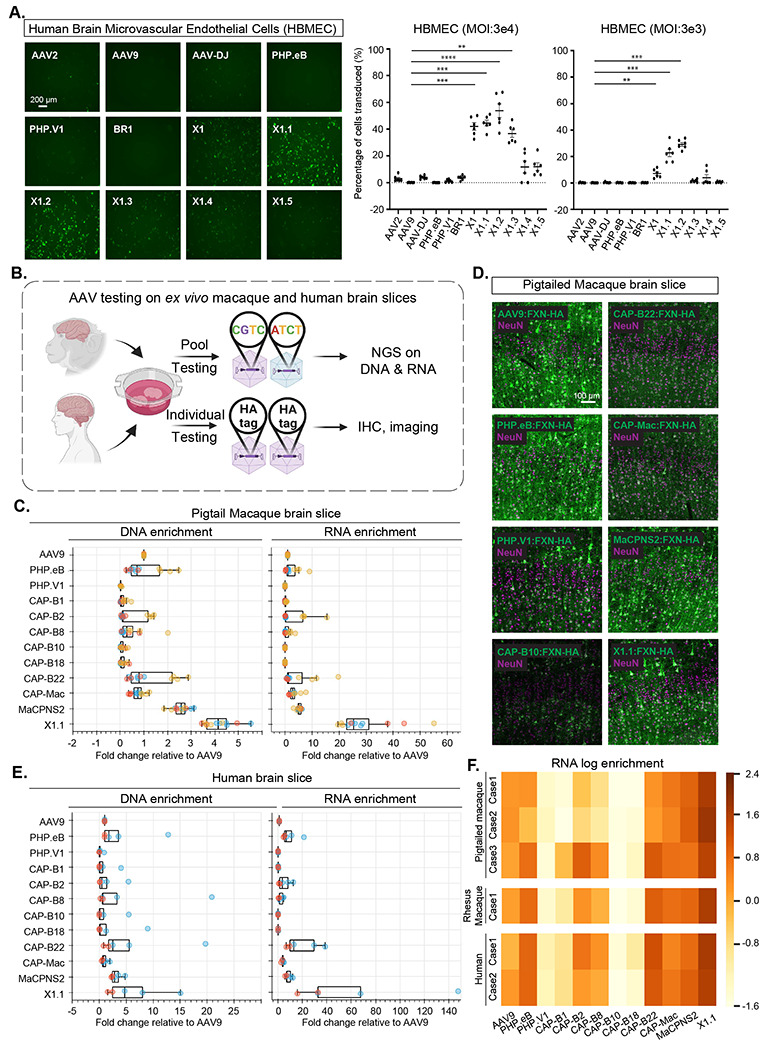
A. (Left) Representative images of AAV (AAV2, AAV9, AAV-DJ, PHP.eB, PHP.V1, BR1, X1, X1.1, X1.2, X1.3, X1.4, X1.5)-mediated eGFP expression (green) in Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells (HBMECs). (AAVs packaged with ssAAV:CAG-eGFP, n= 6 per condition, 1 day expression). (Right) Percentage of cells transduced by the AAVs. In the condition of MOI:3E4, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis test (approximate P<0.0001), and follow-up multiple comparisons with uncorrected Dunn’s test are reported (P=0.0004 for AAV9 versus AAV-X1, P=0.0002 for AAV9 versus AAV-X1.1, P<0.0001 for AAV9 versus AAV-X1.2, P=0.002 for AAV9 versus AAV-X1.3; n=6 per group, each data point is the mean of 3 technical replicates, mean ± s.e.m is plotted). In the condition of MOI:3E3, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis test (approximate P<0.0001), and follow-up multiple comparisons with uncorrected Dunn’s test are reported (P=0.0082 for AAV9 versus AAV-X1, P=0.0004 for AAV9 versus AAV-X1.1, P=0.0001 for AAV9 versus AAV-X1.2; n=6 per group, each data point is the mean of 3 technical replicates, mean ± s.e.m is plotted). **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, ****P ≤ 0.0001 are shown, P > 0.05 is not shown. B. Illustration of AAV testing in ex vivo macaque and human brain slices. The brain slices were freshly extracted from southern pig-tailed macaque brain, rhesus macaque brain, and human brain. The slices were cultured at physiological conditions ex vivo. In the pool testing pipeline (top), a pool of AAVs packaged with CAG-FXN-HA genome containing a unique barcode was applied to the slice, and DNA extraction and RNA extraction were performed after 7 days. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) was performed to determine the proportion of each barcode (AAV) in DNA and RNA. In the individual testing pipeline (bottom), AAVs packaged with CAG-FXN-HA were individually applied to the slices. Fixation, IHC, and imaging were performed on the slices after 7 days. C. DNA and RNA level in southern pig-tailed macaque brain slices for AAVs, with DNA and RNA levels normalized to AAV9. D. Representative images of AAV-mediated CAG-FXN-HA expression in ex vivo southern pig-tailed macaque brain slices. The tissues were co-stained with antibodies against HA (green) and NeuN (magenta). E. DNA and RNA level in human brain slices for AAVs, with DNA and RNA levels normalized to AAV9. F. RNA log enrichment of AAVs across pigtailed macaque, rhesus macaque and human brain slices.
