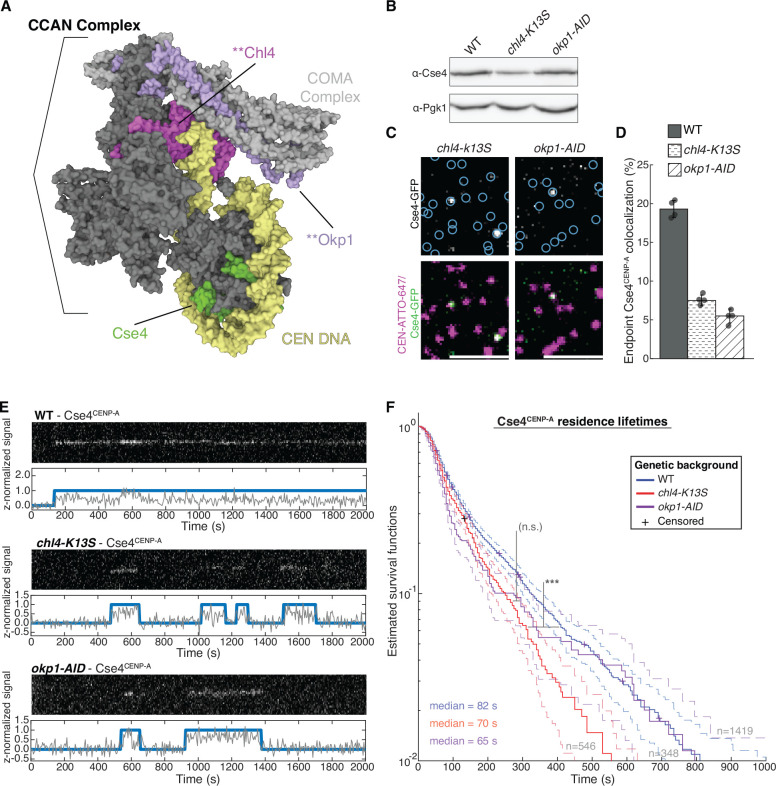
Figure 5. DNA-binding CCAN proteins stabilize the nucleosome to provide a platform for kinetochore assembly.
A Structure of the yeast CCAN in complex with Cse4CENP-A with CEN DNA (yellow), Cse4CENP-A (green), Chl4CENP-N (magenta) and Okp1CENP-Q (purple), highlighting DNA-adjacent regions targeted by the chl4-K13S mutant or proteasomal degradation of Okp1CENP-Q (okp1-AID). Image of 6QLD (Yan et al, 2019) created with Mol* (Sehnal et al, 2021).
B Immunoblot analysis of whole cell extracts from WT, chl4-K13S and okp1-AID cells using indicated antibodies.
C Example images of TIRFM endpoint colocalization assays. Top panels show visualized Cse4CENP-A-GFP on CEN DNA in extracts from chl4-K13S (top-left panel) or auxin-treated okp1-AID strains (okp1-AID, top-right panel) with colocalization shown in relation to identified CEN DNA in blue circles. Bottom panels show overlay of CEN DNA channel (magenta) with Cse4CENP-A-GFP (green), Scale bars 3 μm.
D Quantification of Cse4CENP-A endpoint colocalization with CEN DNA in extracts from WT, chl4-K13S, or okp1-AID genetic backgrounds (19 ± 1.1%, 8 ± 0.7%, 5 ± 0.9%, avg ± s.d. n=4 experiments, each examining ~1,000 DNA molecules from different extracts).
E Representative residence traces of Cse4CENP-A signal on CEN DNA in WT (top), chl4-K13S (middle), or okp1-AID (bottom) extracts. Each example includes kymographs of Cse4CENP-A (488 nm-top) with normalized intensity trace (grey-bottom) as well as identified residences (blue). Images acquired every 5 seconds with normalized fluorescence intensity shown in arbitrary units.
F Kaplan-Meier analysis of Cse4CENP-A residence lifetimes on CEN DNA in extracts from WT (blue - median lifetime of 82 s, n=1419 over 3 experiments of ~1000 DNA molecules using different extracts), chl4-K13S (red – median lifetime of 70 s, n=546 over 3 experiments of ~1000 DNA molecules using different extracts) and okp1-AID (purple – median lifetime of 61 s, n=348 over 3 experiments of ~1000 DNA molecules using different extracts) genetic backgrounds. Significant difference (***) between WT extract and chl4-K13S extract residence lifetime plots (two-tailed p-value of 3.4e-5 as determined by log-rank test). No significant difference (n.s.) between chl4-K13S and okp1-AID residence lifetimes in (two-tailed p-value of .40 as determined by log-rank test). 95% confidence intervals indicated (dashed lines), right-censored lifetimes (plus icons) were included and unweighted in survival function estimates.