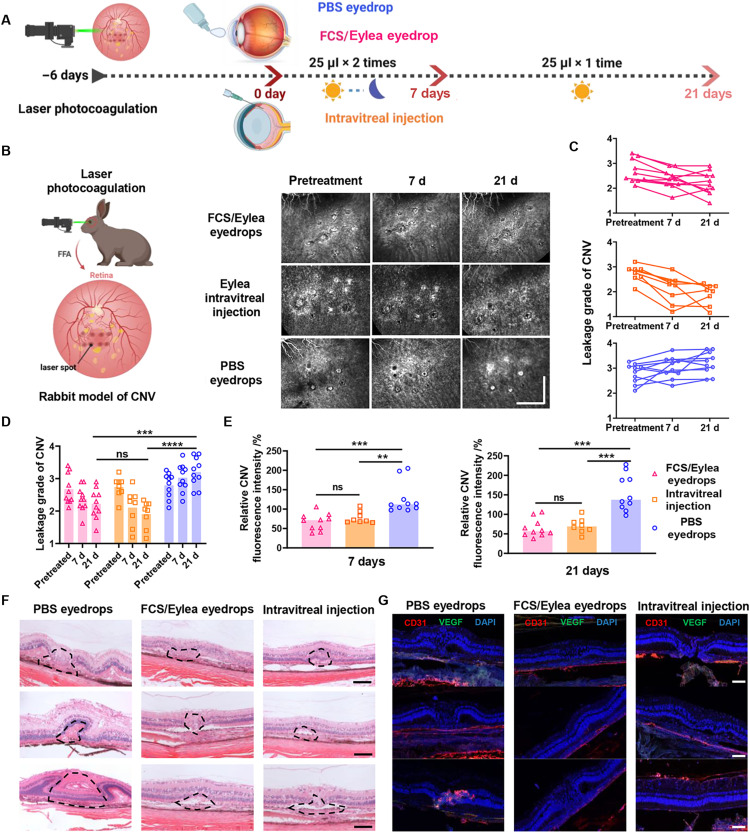
Fig. 7. FCS/Eylea eyedrops for CNV treatment in rabbits.
(A) Schematic illustration of the establishment of NV-AMD in rabbits and the design of animal experiments. The experimental groups included (i) PBS eyedrops, (ii) FCS/Eylea eyedrops, and (iii) intravitreal injection of Eylea. (B) Representative FFA images of individual lesions in CNV-bearing rabbits during treatment on days 0, 15, and 30. Each laser point was indicated in a square (scale bar, 2 mm). (C) Expert grades of leakage in CNV by experienced pathologists in a double-blinded manner in different groups. (D) Statistical analysis of relative fluorescence intensities that present the leakage of angiogenic vessels in each laser point in CNV rabbits with different treatments on days 15 and 30 by ImageJ. (E) Representative H&E staining images of normal and individual lesions in the retina of CNV-bearing rabbits with different treatments (scale bars, 50 μm). (F) Representative immunofluorescence images indicating the expression of VEGF and vascular distribution in individual lesions of CNV-bearing rabbits with different treatments (scale bars, 50 μm). (G) Immunofluorescence staining images of CD31 and VEGF in the retinas of CNV-bearing rabbits with different treatments (scale bars, 50 μm). Data were represented as means ± SD. P values in (D) and (E) were calculated by using one-way ANOVA (**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001).