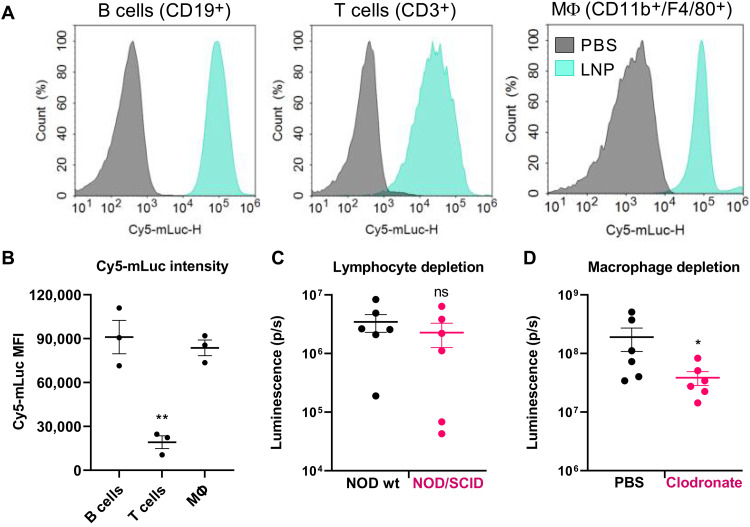
Fig. 6. Peritoneal macrophages contribute to pancreatic mRNA delivery following intraperitoneal administration.
(A) Mice were injected intraperitoneally with LNPs containing Cy5-mLuc (0.5 mg/kg). Immediately after injection, mice were euthanized, and peritoneal wash was collected for flow cytometry analysis. Cy5-mLuc is associated with B cells, T cells, and CD11b+/F4/80+ macrophages. (B) Median fluorescence intensity (MFI) of Cy5-mLuc in B cells, T cells, and CD11b+/F4/80+ macrophages. (C) Lymphocyte trafficking does not facilitate mRNA delivery to the pancreas. Wild-type (wt) NOD mice or NOD/SCID mice that lack mature lymphocytes were intraperitoneally injected with LNPs containing mLuc or Cy5-mLuc (0.5 mg/kg) and euthanized for ex vivo IVIS analysis 3 hours later. There were no differences in either Luc expression or Cy5 distribution to the pancreas resulting from lymphocyte depletion. (D) Mice were injected intraperitoneally with PBS (control) or clodronate liposomes to deplete macrophages. Forty-eight hours later, mice were injected intraperitoneally with mLuc-LNPs, and luminescence in the pancreas was quantified by IVIS. Transfection efficacy decreased in macrophage-depleted mice. Error bars represent SEM. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.005 by one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey’s test.