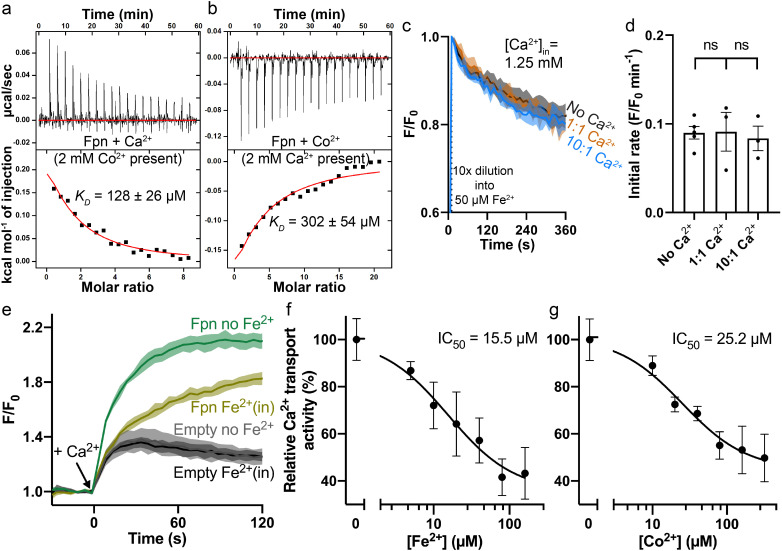
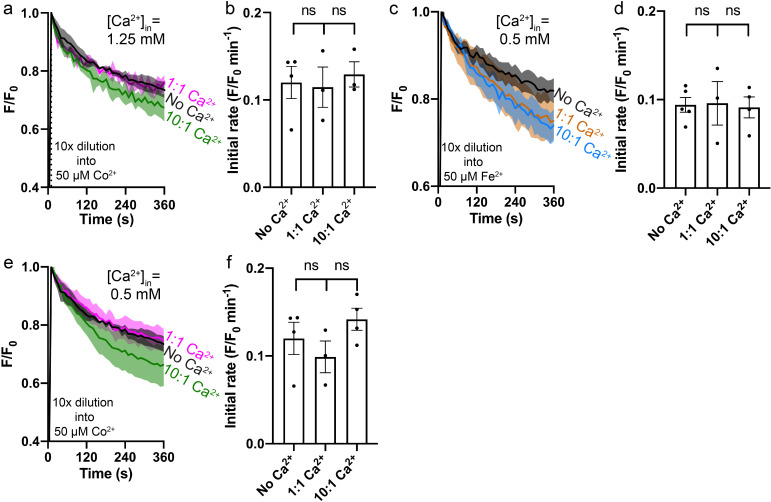
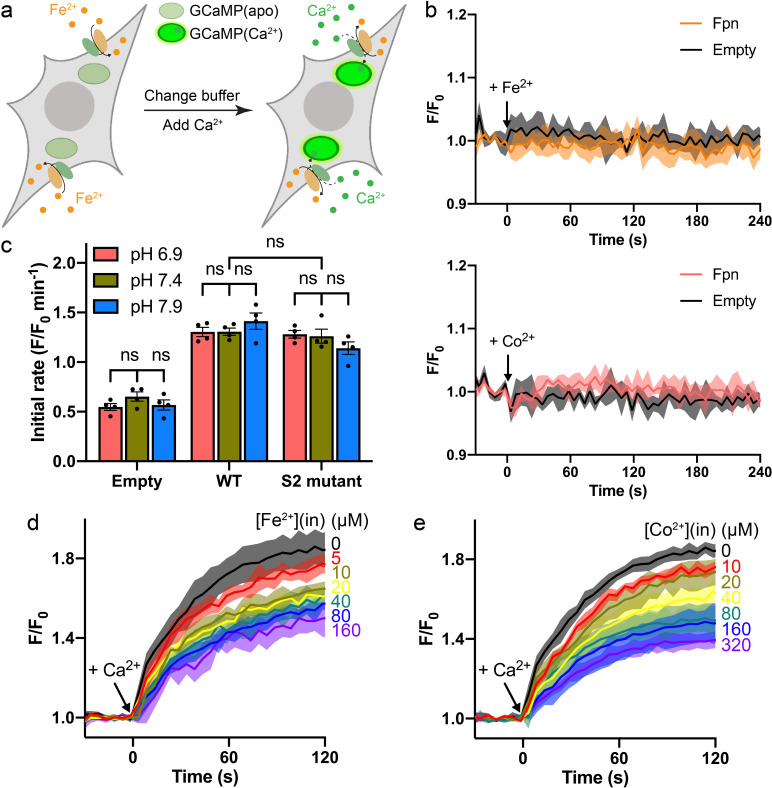
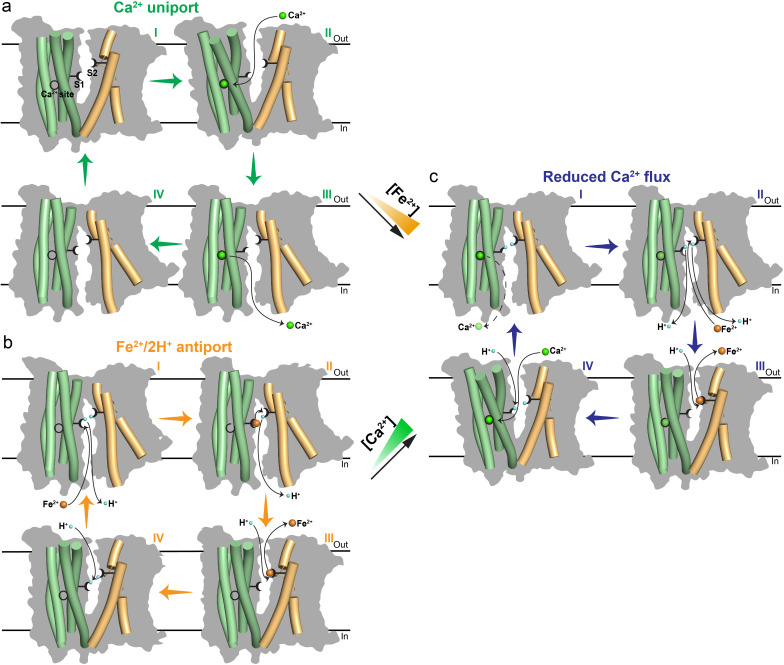
Figure 4. Interplay between Fe2+/Co2+ and Ca2+ in HsFpn.
(a) Ca2+ binding in the presence of 2 mM Co2+. (b) Co2+ binding in the presence of 2 mM Ca2+. (c) Fe2+ transport into proteoliposomes in the presence or absence of Ca2+. The external [Fe2+] is 50 µM. ‘1:1’ indicates symmetrical [Ca2+] at 1.25 mM and “10:1” indicates 1.25 mM Ca2+ inside and 0.125 mM Ca2+ outside. 1 mM sodium ascorbate was included in all samples. All fluorescence traces are subtracted from corresponding blank controls using vesicles with no HsFpn. (d) Comparison of initial rates of Fe2+ transport in (c). One-way ANOVA was used for statistical analysis. (e) Ca2+ (1 mM) uptake by HEK cells expressing HsFpn in the presence (dark yellow) or absence (green) of 80 µM Fe2+ that has been pre-loaded into the cells. Uptake is monitored by jGCaMP7s which is co-expressed in cytosol. Cells transfected with an empty vector (dark and light gray) serve as negative controls. Ca2+ transport at different concentrations of Fe2+ (f) or Co2+ (g). Normalized initial rates of Fpn-specific Ca2+ uptake were used to represent relative Ca2+ transport activities. Data were fitted (black solid line) to an inhibitory dose-response equation to calculate IC50 values.