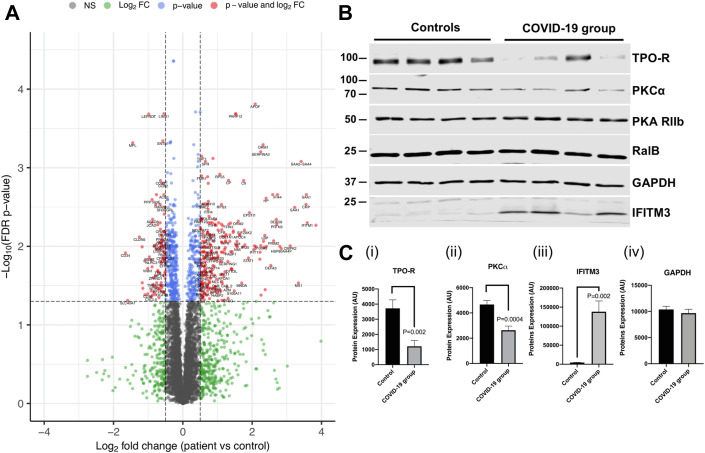
Figure 1.
The platelet proteome is altered in patients with COVID-19. (A) Volcano plot of the proteins altered in platelet lysates from patients (N = 7) and controls (N = 6) using tandem mass tag proteomics. Protein changes were analyzed by Welch’s t-test. The proteins that had both a log2 fold change (logFC) greater than ± 0.5 and a false discovery rate–adjusted p value less than .05 are shown in red. Proteins with only a false discovery rate p value less than .05 are shown in blue. The proteins indicated in blue and red make up the 858 proteins that were altered in amount in COVID-19 compared with control patients. Proteins that only had logFC greater than ± 0.5 are shown in green. Proteins that did not reach the p value or logFC threshold are shown in gray. One protein was excluded from the figure (which had a logFC of over −4) to be able to see other data points more clearly. Plot was made using the Enhanced Volcano R package (https://github.com/kevinblighe/EnhancedVolcano). (B) Representative Western blot using platelet lysates from 4 controls and 4 patients for the TPO receptor, PKCα, PKA (control), RalB, GAPDH (control), and IFITM3. Analyses were performed using Student’s t-test. (C) (i) Western blot quantification of the TPO receptor (mean + SEM, N = 9). (ii) Western blot quantification of PKCα (mean + SEM, N = 9). (iii) Western blot quantification of IFITM3 protein expression (mean + SEM, N = 8). (iv) Western blot quantification of GAPDH loading control (mean + SEM, N = 8, p = .58).