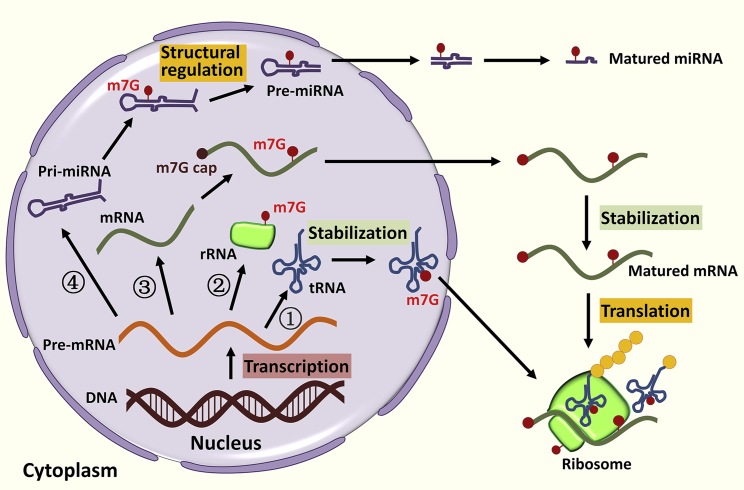
Figure 2.
The functions of m7G methylation in RNA metabolism
m7G methylation is involved in multiple steps of RNA metabolism processes. First, G46 on tRNA can be methylated by METTL1/WDR4 complex and conferred with positive charge via hydrogen bonding to bases G22 and C13, stabilizing the tRNA three-dimensional core of tRNA. Second, rRNA m7G can be methylated by WBSCR22/TRMT112 complex at human small ribosomal subunit rRNA G1639 with uncertified function. Third, mRNA m7G can be methylated by METTL1/WDR4 complex, leading to stabilization and translation of mRNA. Fourth, m7G of pri-let-7e-5p can also be methylated by METTL1/WDR4 complex, which, destabilizes G-quadruplexes and thereby promotes DROSHA-mediated cleavage of primary miRNA transcripts.