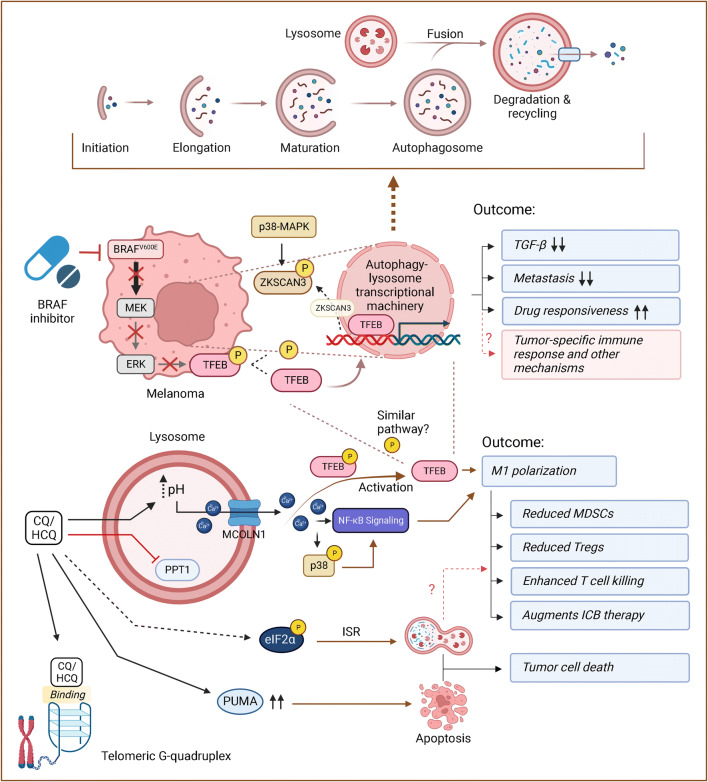
Figure 1.
Dynamic roles of autophagy in melanoma. (1) Schematic representation of autophagy process. (2) BRAFi induces transcriptional activation of autophagy-lysosome program (by disrupting ERK-mediated TFEB phosphorylation and promoting p38-MAPK-mediated phosphorylation/inactivation of the autophagy repressor ZKSCAN3) and its blockade causes tumor progression, metastasis, and drug resistance that is associated with enhanced TGF-β signaling. (3) CQ modes of action in addition to inhibition of autophagy flux. This includes but not limited to TFEB activation and nuclear translocation (in part, by pH-dependent calcium release through MCOLN1), p38 and NF-κB signaling activation (following calcium release) and consequent macrophage polarization (from M2 to M1) and associated increased anti-tumor immunity, telomeric G-quadruplex binding, PUMA stabilization and induced apoptosis, as well as ISR activation (through eIF2α phosphorylation). MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; p38-MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; TFEB, transcription factor EB; ZKSCAN3, zinc finger with KRAB and SCAN domains; CQ/HCQ, chloroquine/hydroxychloroquine; MCOLN1, Mucolipin-1; PPT1, Palmitoyl-protein thioesterase 1; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; MDSCs, myeloid-derived suppressor cells; Tregs, regulatory T cells; ISR, integrated stress response; PUMA, p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis. This figure was created with BioRender.com.