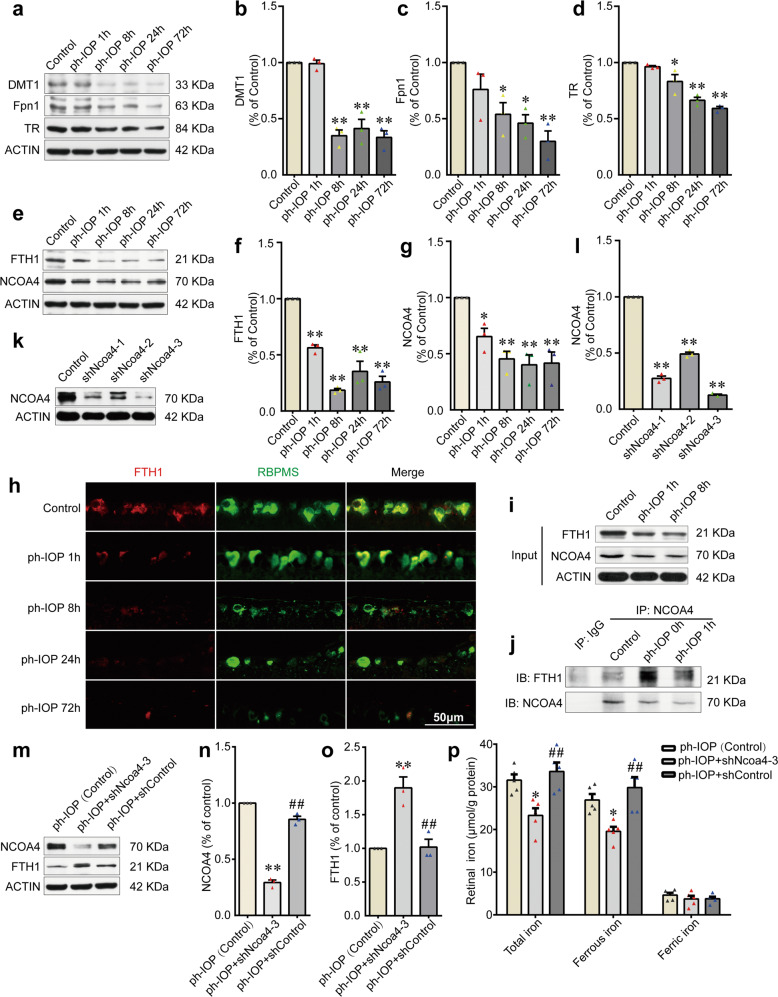
Fig. 2. NCOA4-mediated FTH1 degradation led to pathologically high intraocular pressure (ph-IOP)-induced iron accumulation in retinas.
a–d Western blotting detection of the retinal levels of DMT1, Fpn1, and TR (normalized to that of actin) in control and ph-IOP injured mice (n = 3 in each group). e–g Western blotting detection of the retinal levels of FTH1 and NCOA4 (normalized to that of actin) in control and ph-IOP injured mice (n = 3 in each group). h Representative photomicrographs of immunofluorescence staining for FTH1 (red) in retinal ganglion cells (counterstained with RBPMS; green). I, j Co-immunoprecipitation showing the endogenous interaction between NCOA4 and FTH1 in control and ph-IOP injured mice. k, l Western blotting detection of the retinal levels of NCOA4 (normalized to that of actin) in mice receiving pAAV-spgRNA-EGFP (control) and pAAV-shNcoa4-EGFP injection for 3 weeks (n = 3 in each group). m–o Western blotting detection of the retinal levels of NCOA4 and FTH1 (normalized to that of actin) in ph-IOP injured mice, with or without AAV-mediated Ncoa4 knockdown at 1 h after modeling (n = 3 in each group). p Retinal iron contents in ph-IOP injured mice, with or without AAV-mediated Ncoa4 knockdown, at 1 h after modeling (n = 5 in each group). DMT1, divalent metal transporter 1; Fpn1, ferroportin 1; FTH1, ferritin heavy polypeptide 1; NCOA4, nuclear receptor coactivator 4; TR, transferrin receptor. Data are shown as the mean ± SD; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 (compared with the control group using one-way analysis of variance); ##p < 0.01 (compared with the shNcoa4 group using one-way analysis of variance). Bar = 50 μm.