Figure 5.
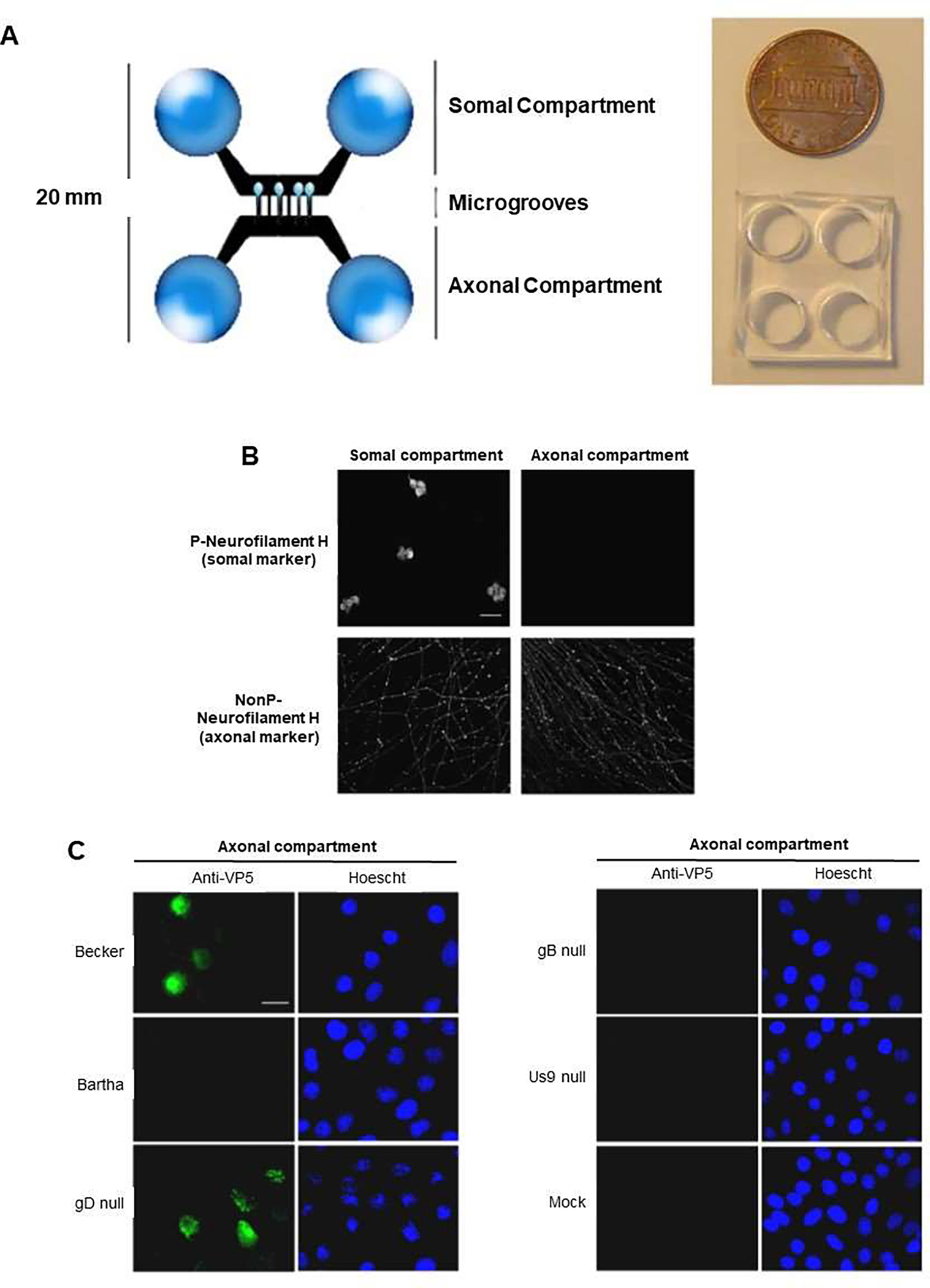
Microfluidic chamber infected by pseudorabies virus (PRV) to study neuron-to-cell spread of infection and viral transport in axons. (A) Microfluidic chamber system, in which chambers were fabricated from polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), and connected by 450 mm in length, and 10 mm in width microgrooves. PDMS was attached to a glass coverslip. Somal compartment contained rat superior cervical ganglia (SCG) neurons, and the axonal compartment conducted axonal growth via the microgrooves. SCG neurons cultured in the chamber, polarized and matured after 9 d. (B) Confocal microscopy images showing neurons in the chamber, fixed and stained for phosphorylated neurofilament H, a somato-dendritic marker, and non-phosphorylated (NonP) neurofilament H, an axon-specific marker. (C) Epifluorescent and Hoechst images of PK15 cells in the axonal compartment stained with antibodies against the VP5 capsid protein at 20 h after infection. Neurons in the somal compartment are not shown. Reproduced from [42], which is an open access article distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
