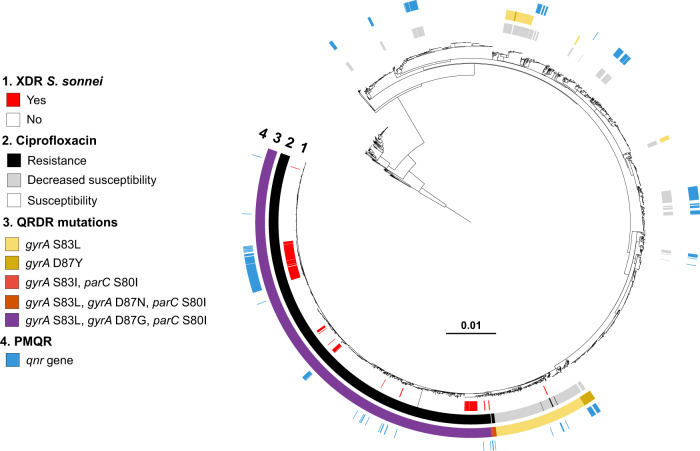
Fig. 4. Acquisition of genes encoding resistance to quinolones and fluoroquinolones in our genomic dataset.
Maximum-likelihood phylogeny of 3141 S. sonnei genomic sequences as shown in Fig. 2. The rings show the associated information (see key) for each isolate, according to its position in the phylogeny, from the innermost to the outermost, in the following order: (1) the XDR isolates; (2) antimicrobial susceptibility testing for ciprofloxacin (resistance defined as minimum inhibitory concentration [MIC] ≥ 1 mg/L; susceptibility as MIC ≤ 0.06 mg/L; decreased susceptibility as MIC between 0.12 and 0.5 mg/L); (3) mutations in the quinolone resistance-determining region (QRDR) of gyrA and parC; (4) presence of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance (PMQR) genes of the qnr family.