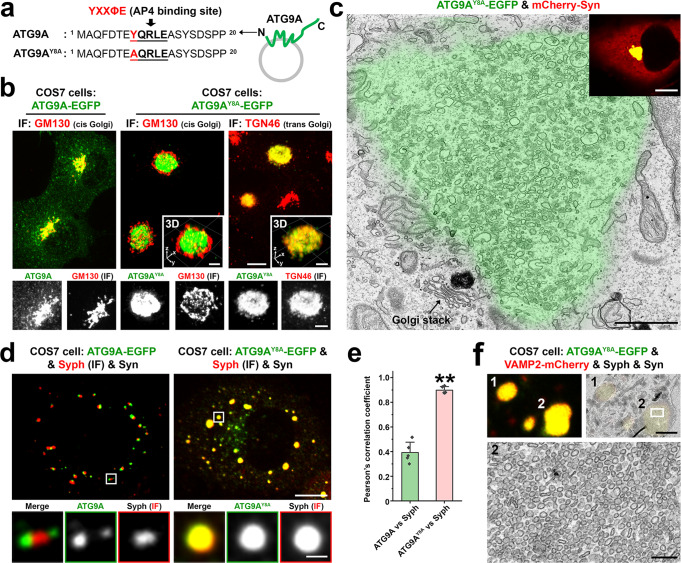
Fig. 7. Impact of the Y8A mutation of ATG9A on its sorting and segregation from synaptophysin.
a Amino acid sequence of the cytosolic N-terminal region of ATG9A with the AP4-binding motif in bold characters. b COS7 cells expressing ATG9A-EGFP (WT) or ATG9AY8A-EGFP and immunostained for cis-Golgi (GM130) and trans-Golgi (TGN46) markers, showing that ATG9AY8A is retained in the TGN area, where it colocalizes with TGN46. See also Supplementary Video 5. c Correlative light-electron microscopy (CLEM) of a COS7 cell expressing ATG9AY8A-EGFP and mCherry-synapsin, showing that the accumulation of ATG9AY8A in the TGN area (green color from the fluorescence image) correlates with a massive accumulation of small heterogeneously sized vesicular-tubular structures in the same area. An arrow points to a Golgi stack. The inset shows that synapsin is colocalized with ATG9AY8A in the TGN area, while no sparse droplets positive for ATG9AY8A and for synapsin are present in this cell. d COS7 cell triple transfected with synapsin, synaptophysin and either ATG9A-EGFP or ATG9AY8A-EGFP. Synaptophysin was detected by immunofluorescence. ATG9AY8A-EGFP failed to form distinct clusters within synapsin condensates and completely intermixed with synaptophysin. e Colocalization analysis of synaptophysin vs. either ATG9A (WT) or ATG9AY8A in COS7 cells also expressing synapsin. Values are means ± SD. **p < 0.01 by the two-sided Student’s t-test (droplets in 5 cells for each condition were analyzed). f CLEM image of a COS7 cell quadruple transfected with ATG9AY8A-EGFP, VAMP2-mCherry, synaptophysin and synapsin. Top images show corresponding light microscopy and EM fields and the bottom image shows a detail of droplet #2 at high magnification. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. Scale bars, b = 10 μm (5 μm for insets and enlarged images), c = 1 μm (10 μm for inset), d = 10 μm (1 μm for enlarged images), f = 2 μm (200 nm for the enlarged image at the bottom). p-value (e): 1.322 × 10‒6.