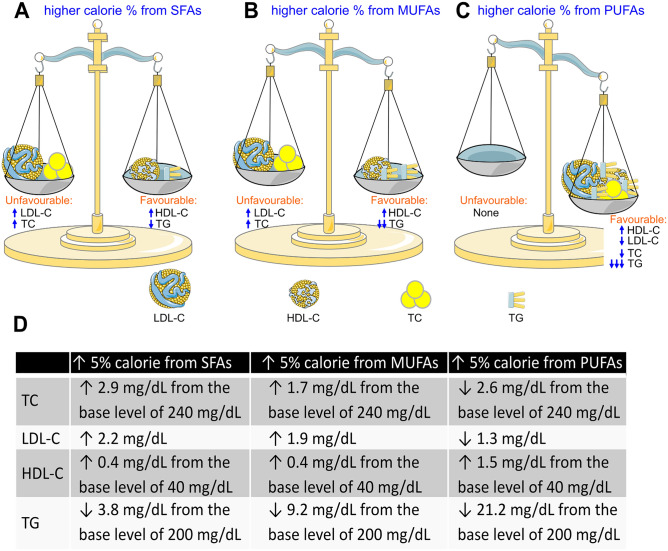
Figure 1.
Lipid profile associated with usual intake of fatty acids in 44,279 adults without a prior diagnosis of myocardial infarction. (A-B), Higher usual intake of saturated fatty acids (SFAs, A) and monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs, B) was associated with higher low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), higher total cholesterol (TC), higher high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) and lower triglyceride (TG). (C), Higher usual intake of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) was associated with higher HDL-C, lower LDL-C, lower TC, and lower TG. (D) The extent of change in lipid profile associated with a 5% higher calorie intake from fatty acids. This figure was partly generated using Servier Medical Art, provided by Servier, licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 unported license.