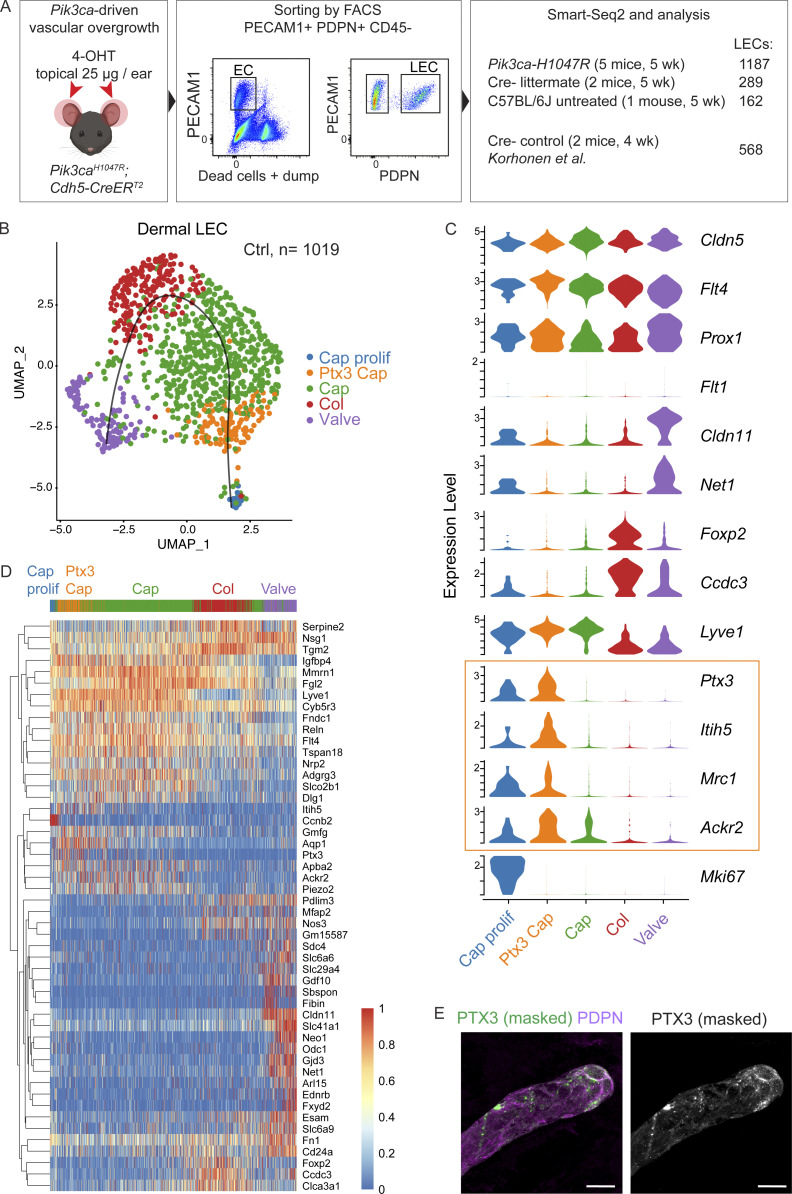
Figure 5.
Definition of dermal LEC subtypes by single cell transcriptomics. (A) Schematic overview of dermal LEC isolation for scRNA-seq. (B) The five dermal LEC clusters from control ear skin visualized in a UMAP landscape, labeled by cluster assignment. Black line depicts trajectory calculated from UMAP embedding (unsupervised Slingshot algorithm). (C) Violin plots showing the expression of selected pan-EC, LEC, and BEC markers, as well as LEC subtype marker genes in the five clusters. Note a new LEC subtype (immune-interacting LECs, iLECs; yellow box) defined by the expression of Ptx3, Itih5, and Mrc1 that are also expressed in Ptx3-LECs in the lymph node. (D) Heatmap showing the expression of zonation markers across the five LEC clusters. Cells were ordered by the trajectory. Color indicates read counts in log-scale. (E) Whole-mount immunofluorescence of non-permeabilized ear skin showing extracellular PTX3 staining predominantly at capillary terminals. IMARIS surface mask based on podoplanin (PDPN) expression was used to extract LEC-specific PTX3 signal. The original unmasked image is shown in Fig. S4 E. Scale bar: 20 μm (H).