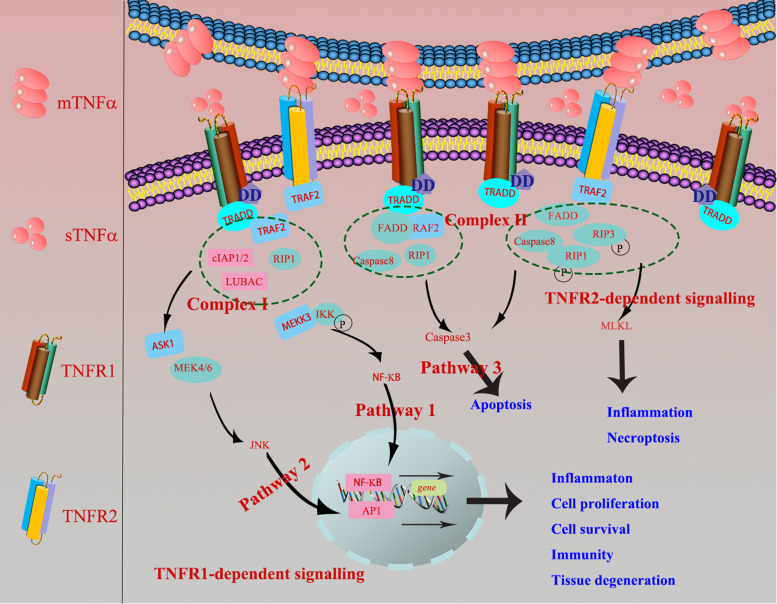
Fig. 1.
TNF-R1-dependent signalling: once TNF-R1 binds mTNF-α or sTNF-α, it recruits the adaptor protein TRADD or FFADD via its DD motifs. Subsequently, it recruits complex I, namely serine/threonine kinase receptor interacting protein-1 (RIP-1), TNF-R-associated factor 2 (TRAF-2), as well as cIAP1 and cIAP2. Then, it activates NF-κB and JNK/AP1 signalling pathways and medicates the expression of targeted genes, finally involves in various biological processes, inducing inflammation, tissue degeneration, host defence, cell proliferation, cell survival and immunity. Besides, TRADD can also recruit and form the complex II (FADD, RIP-A, TRAF-2 and caspase 8) to finally activate caspase 3 eliciting cell apoptosis (Ref. 2). TNF-R2-dependent signalling: TNF-R2 is restricted to bind with mTNF-α, primarily recruiting TRAF-2 via its TRAF domain, which further causes the recruitment of complex II and activation of apoptosis, inflammation and necroptosis.