Fig. 7. Moderate, voluntary, intermittent running exercise (RE) enhanced hippocampal neurogenesis in rats with Gulf War Illness (GWI).
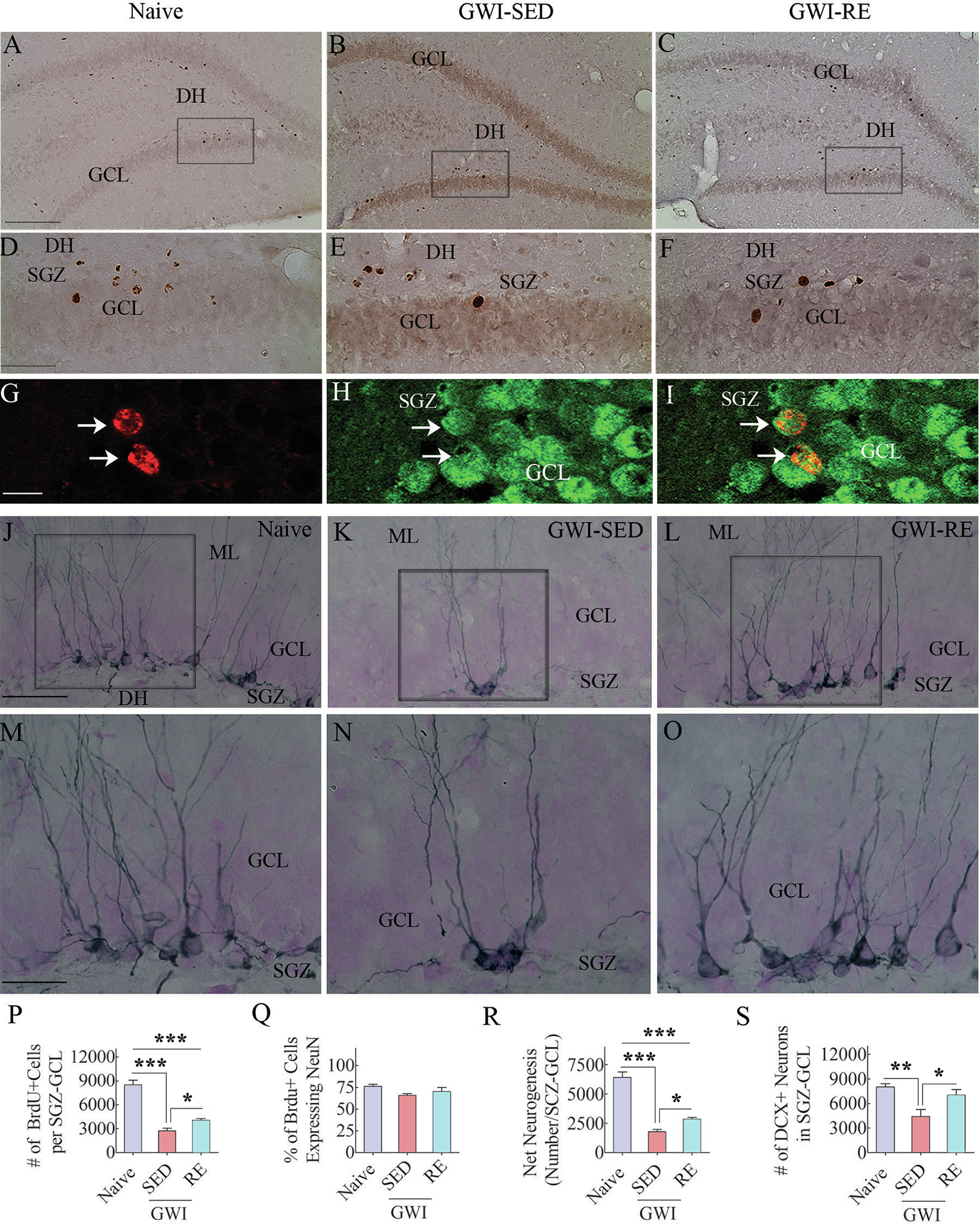
Figures in A-C show examples of 5′-bromodeoxyuridine-positive (BrdU + ) cells in the subgranular zone-granule cell layer (SGZ-GCL) of the hippocampus from a naïve control rat (A), a sedentary GWI rat (GWI-SED; B), and a GWI rats that performed RE (GWI-RE, C). D, E, and F are magnified views of regions from A, B, and C. Figures G-I illustrate examples of BrdU + cells expressing neuron-specific nuclear antigen (NeuN, arrows). The bar charts P-R compare the number of BrdU + newly born cells (P), the percentage of BrdU + cells that differentiated into NeuN + neurons (Q), and net neurogenesis (R) in the SGZ-GCL of the hippocampus between different groups. Figures J-O illustrate the distribution of doublecortin-positive (DCX + ) newly born neurons in the SGZ-GCL of the hippocampus from a naïve control rat (J), a GWI-SED rat (K), and a GWI-RE rat (L). M–O are magnified views of regions from J-L. The bar chart S compares the number of DCX + neurons across groups. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001. GCL, granule cell layer; ML, molecular layer; DH, dentate hilus; SGZ, subgranular zone. Scale bar, A-C = 200 μm; D-F = 50 μm; G-I = 25 μm; J-L = 50 μm; M–O = 25 μm.
