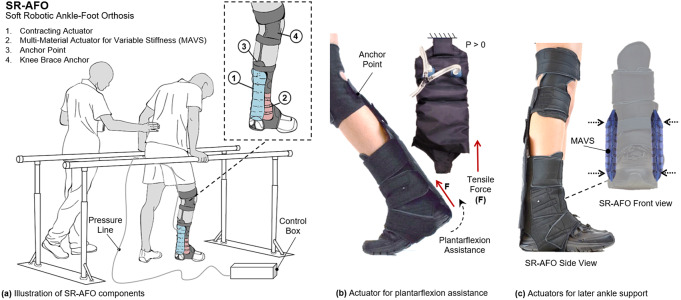
Figure 1.
(a) The concept illustration of a soft robotic ankle-foot orthosis (SR-AFO) that assists walking with active ankle plantarflexion assistance as well as medial/lateral ankle support. Since the SR-AFO is designed to be used in its current stages as a rehabilitative device in clinical trials, the goal is to have the participant in a rehabilitative space already equipped with pressure lines, and the hardware needed to control pressure, timing, and record data from each session will sit beside the participant. Ideally, in most cases, there would be no compressor in this setup, rather the electropneumatic hardware box would connect directly to line pressure from the wall. (b) The actuators used for plantarflexion assistance are placed on the back of the leg, and contract to pull the heel upward. (c) The actuators to provide lateral ankle support are placed on either side of the ankle joint, and act as a brace when active to provide variable stiffness to the joint.