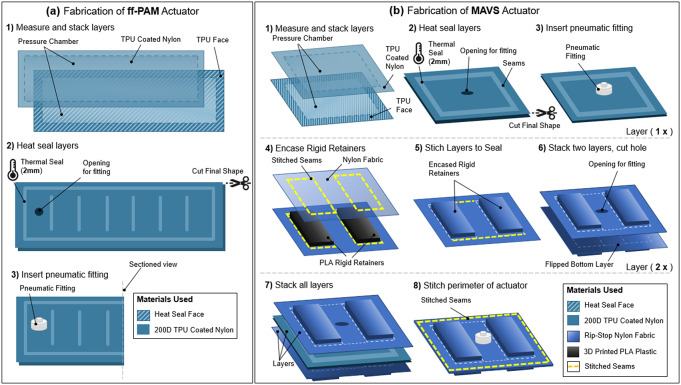
Figure 10.
(a) The fabrication process of the flat fabric pneumatic artificial muscle actuator. The formation of the air-tight chamber using thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU)-coated Nylon and a heat seal (a1), the creation of the ribs and placement of the pneumatic fitting (a2), and the final fitting placement (a3) are illustrated. (b) The fabrication process of the MAVS actuator. Heat sealing and fitting placement of the soft actuator using TPU-coated Nylon to form the air-tight chamber (b1–b3), the laying and placement of the rigid retainers in the out layers of the MAVS by embedding polylactic acid (PLA) into Nylon fabric layers (b4–b6), and the final stages of integrating and stacking the MAVS layers (b7 and b8) are shown where the air-tight chamber is placed in between two layers of PLA embedded in Nylon. All components are stitched together around the perimeter to form the MAVS.