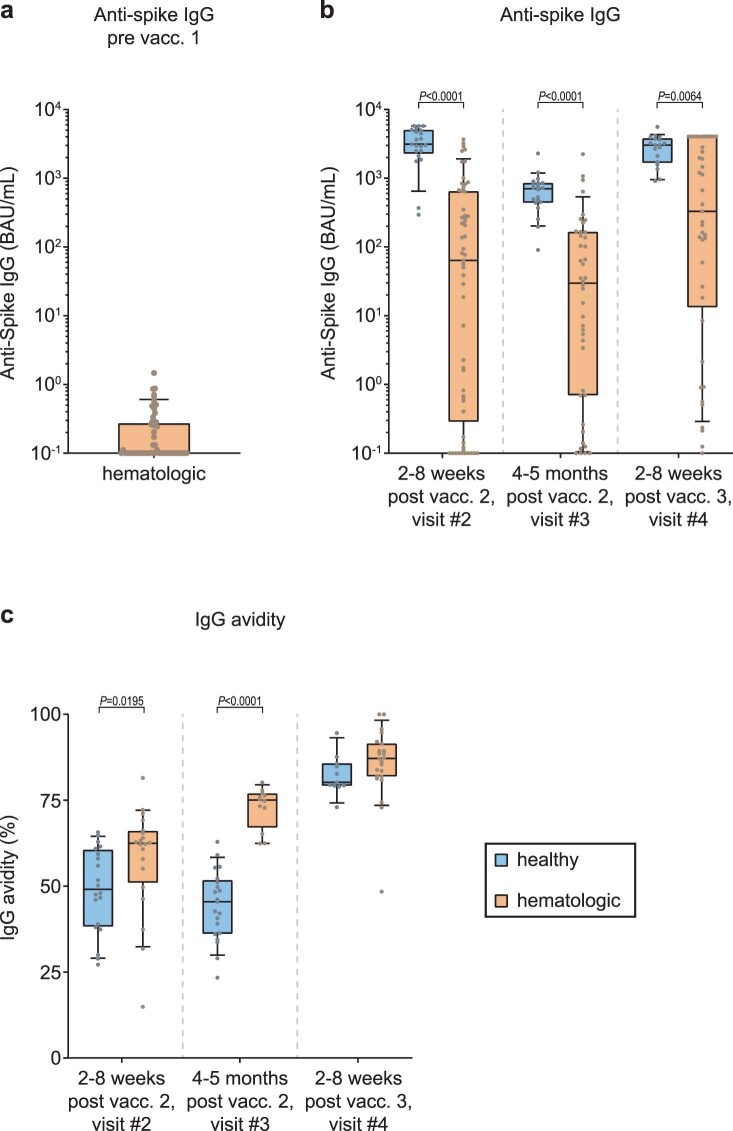
Extended Data Fig. 1. Comparison of IgG-type antibody levels and avidity in healthy individuals and patients with hematologic neoplasia at different time points before and after COVID-19 vaccination.
Data is depicted as boxplots with median, bounds between upper and lower quartiles, and whiskers between the 10th and 90th percentile. Differences between groups (healthy individuals/ patients with hematologic malignancies) were analyzed for statistical significance using the Mann-Whitney test. Brackets show statistically significant differences. Absence of brackets or p-values indicate absence of significance. a, Anti-spike S1 domain IgG titers in BAU/mL prior to vaccination in patients with hematologic malignancies (n = 56). b, Anti-spike S1 domain IgG antibody levels at different time points after COVID-19 vaccinations #2 and #3 in healthy individuals (visit #2/ visit# 3/ visit #4: n = 21/20/19, respectively) and in cancer patients (visit #2/ visit# 3/ visit #4: n = 57/42/42, respectively). c, Anti-spike IgG antibody avidity at different time points after vaccinations #2 and #3. Healthy individuals: visit #2 (n = 20)/ visit #3 (n = 21)/ visit #4 (n = 11); Hematologic malignancies: visit #2 (n = 20/ visit #3 (n = 12)/ visit #4 (n = 23).