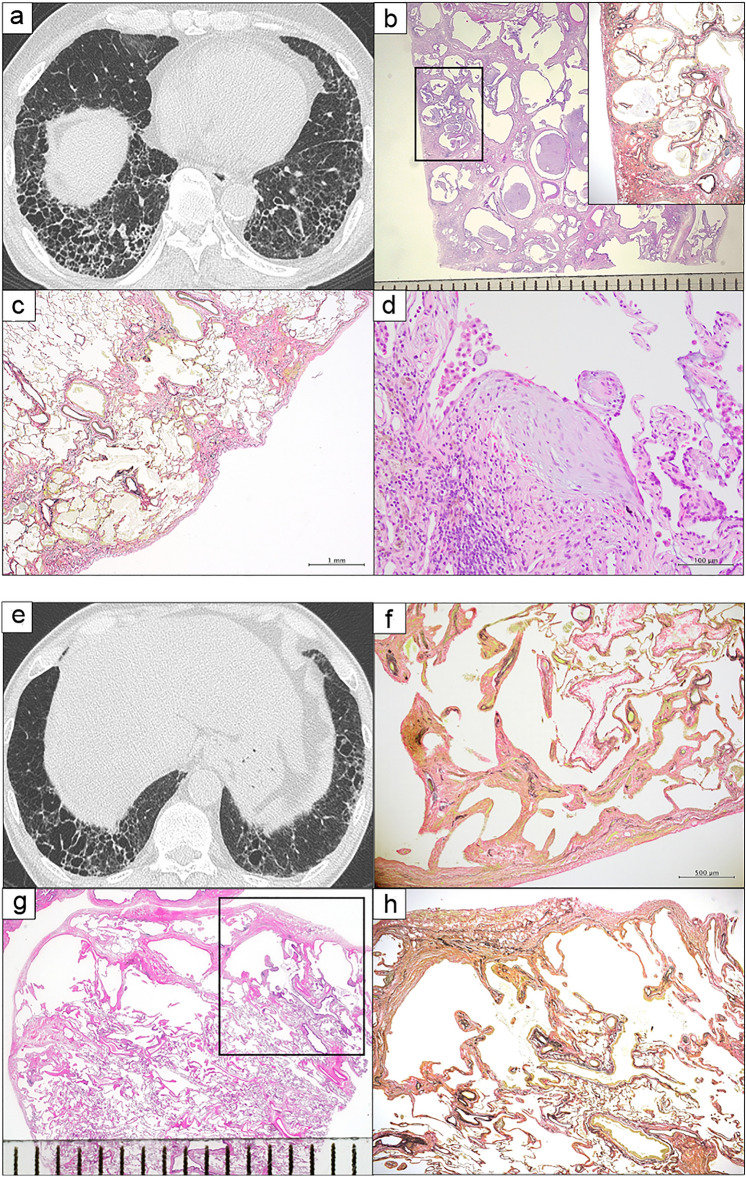
Fig. 2.
Comparison of HRCT scan findings and histopathological patterns between patients diagnosed with IIP and those with pathological non-ILD. a–d. An IIP case. a The UIP pattern on HRCT: presence of honeycombing with sub-pleural and basal predominance. b Panoramatic view (scale bar: 1 mm) and low-magnification photograph (box) (Elastica van Gieson staining) showing dense fibrosis with architectural distortion in the form of honeycomb change. c Low-magnification photomicrograph showing predominant sub-pleural and para-septal distribution of fibrosis (scale bar: 1 mm, H & E). d Higher-magnification photomicrograph showing fibroblast foci (scale bar: 100 µm, H & E).e–h. A pathological non-ILD case. e Indeterminate UIP pattern on HRCT: multiple thin-walled cysts in the lower lobe. f High magnification photomicrograph showing mild fibrosis with centriacinar emphysema in the background (scale bar: 500 µm, Elastica van Gieson stain). g Panoramatic view (scale bar: 1 mm) and h low-magnification photomicrograph (box in Fig. 4 g) (Elastica van Gieson staining) showing a fibrous wall of bronchiolocentric cysts. HRCT: high-resolution computed tomography, IIP: idiopathic interstitial pneumonia, ILD: interstitial lung disease, UIP: usual interstitial pneumonia