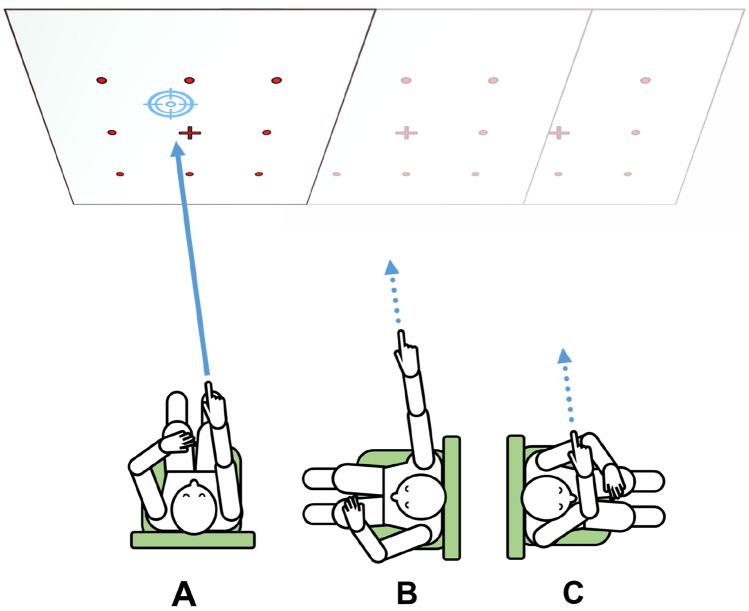
Fig. 2.
Illustration of the 3D-finger arm pointing paradigm. While the subject with eyes open was seated on a swivel chair in a standardized centered position in front of a white wall with a nine-point matrix marked on it, the pointing device is calibrated to each point in a randomized order. Afterwards, the subject was asked to point to each target in five conditions with the eyes closed and the body in a neutral position straight ahead, b 90° rotation to the non-dominant side, back in neutral position (a), c 90° rotation to the dominant side resulting in elbow flexion, and back in neutral position (a). The tasks performed in neutral position are used to calculate deviations due to task repetitions, while the performance in position b, c allow determination of deviations due to spatial transformation of body-to-wall position