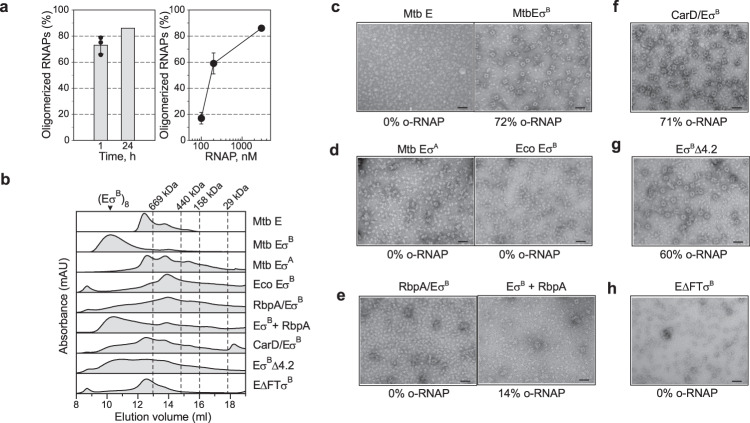
Fig. 5. Regulation of the EσB octamer assembly in vitro.
a Time (left panel) and concentration (right panel) dependence of the EσB octamer assembly. Bar graphs show the percentage of RNAP molecules assembled in octamers relative to the total number of RNAP molecules visualized on the EM grid. Values were calculated from the negatively stained images by counting particles using the EMAN2 e2boxer module. When indicated, data are presented as mean values ± SD calculated from n = 3 (bar graph) and n = 4 (line graph) representative images. b Assessment of the RNAP oligomerization state by SEC. Elution profiles of the RNAP core (E) in complex with a different set of transcription factors (indicated on the right) match combinations shown in c–h. The octamer peak is indicated as (EσB)8. Dashed lines indicate the position of the molecular weight markers: 669 kDa, thyroglobulin; 440 kDa, ferritin; 158 kDa, aldolase; 29 kDa, carbonic anhydrase. c Negatively stained images of the Mtb RNAP core (Mtb E) and Mtb RNAP holoenzymes (Mtb EσB). d Negatively stained images of Mtb EσΑ and of the hybrid RNAP holoenzyme assembled from σB and E. coli RNAP core (Eco EσB). e Negatively stained images of Mtb EσB. RbpA was added to E before assembly with σB (RbpA/EσB) and after the octamer formation (EσB + RbpA). f Negatively stained images of Mtb EσB formed in presence of CarD (CarD/EσB) added to E before assembly with σB. Negatively stained images of mutant EσB harboring a deletion in the σΒ subregion 4.2 (EσBΔ4.2) (g) or a deletion in the β flap (EΔFTσB) (h). Scale bar in c–h = 50 nm. Experiments in c–h were repeated independently at least twice with similar results. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.