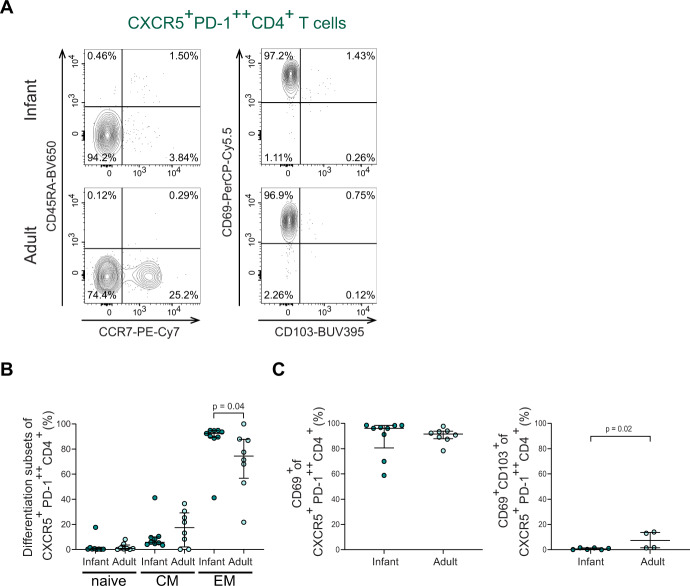
Fig. 2.
Infant intestinal CXCR5+PD-1++ CD4+ T cells exhibit a tissue-resident memory phenotype. A Representative flow cytometric plots to define i) left: memory subsets based on CCR7 and CD45RA expression in CXCR5+PD-1++ CD4+ T cells and ii) right: CD103 and CD69 expression on CXCR5+PD-1++ CD4+ T cells. B Frequencies (%) of naive (CCR7+CD45RA+), central memory (CCR7+CD45RA−) and effector memory (CCR7-CD45RA−) T cell populations in CXCR5+PD-1++CD4+ T cells comparing infant and adult intestines. C Frequencies (%) of CD69+ cells and CD69+CD103+ cells within CXCR5+PD-1++ CD4+ T cells comparing infant and adult intestines. Medians and IQRs are depicted in all figures. (For B and C left: infant n = 9; adult n = 8. For C right: infant n = 6; adult n = 4). Mann–Whitney test was used to compare infant and adult samples. Only significant p values are shown