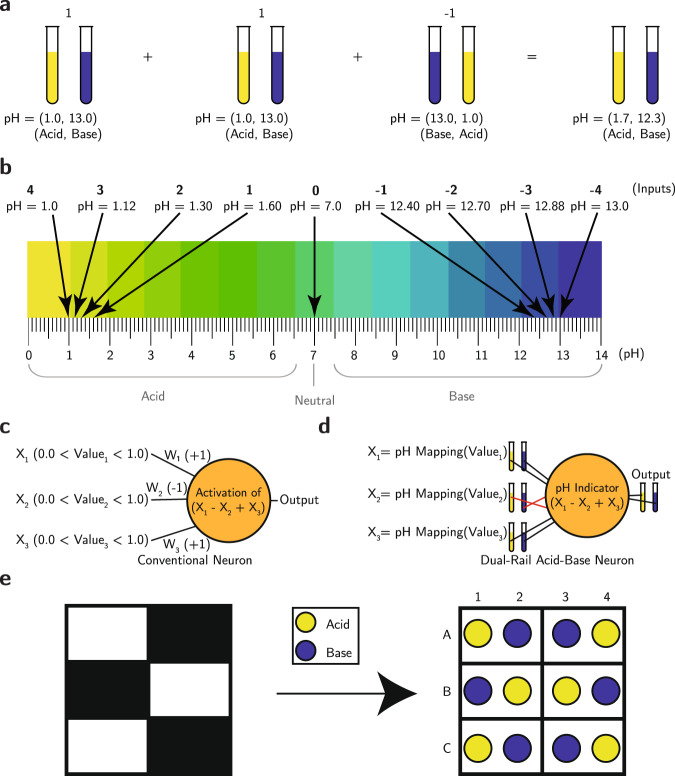
Fig. 1. Method overview.
a The dual-rail acid-base encoding for an addition followed by a subtraction (using the inverted representation). Each “1” is represented by an acidic solution (on the pH rail) and a basic solution (on the complementary pH rail); a “−1” is represented by the same solutions in reverse order. b Illustration of the mapping of discretized inputs into their corresponding pH values. c Conventional neuron with its default operations. d Equivalent neuron using an acid-base encoding with analog input values mapped to the corresponding pH value from the calculated range. Crossing lines indicate multiplying by −1. e Encoding of a 2 × 3 binary array of pixels into a well plate of acids (yellow) and bases (blue), where each pixel value is mapped to two wells.