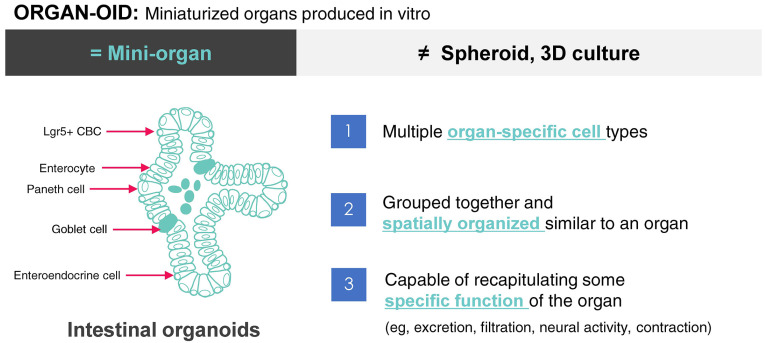
Fig. 1.
Definition of organoid. An organoid is in vitro miniaturized and simplified three-dimensional (3D) structure having multiple organ-specific cell types constituting the organ. For example, intestinal organoids are composed of enterocytes, Paneth ells, goblet cells, enteroendocrine cells and stem cells (Lgr5+ crypt base columnar cells), which constitute the actual intestinal epithelium. In addition, organoid have organ-like structures (e.g., crypt and villus structures in intestinal organoids) and mimic their specific functions (e.g., secretory and absorptive functions in intestinal organoids).