Figure 2.
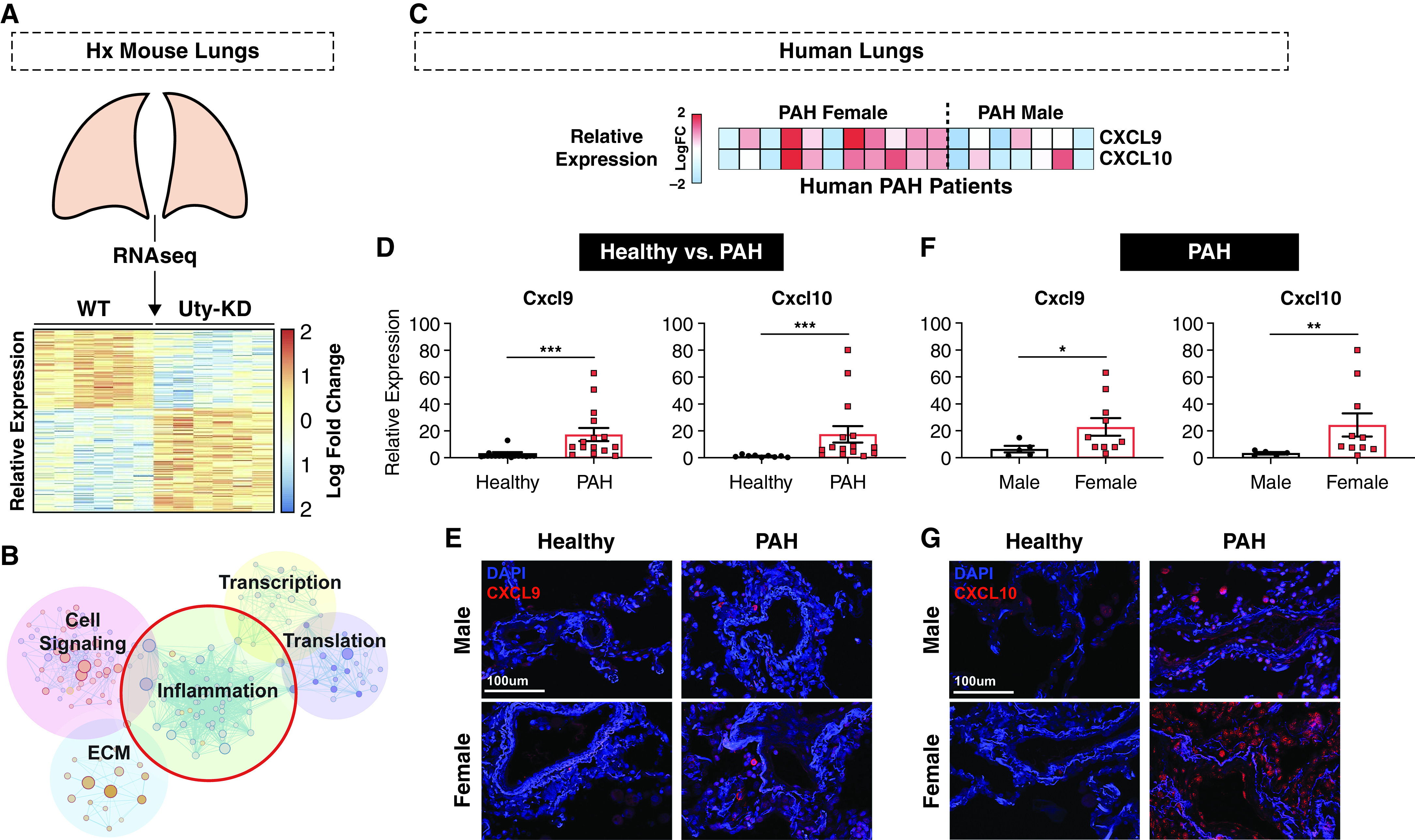
Proinflammatory chemokines CXCL9 and CXCL10 are autosomal downstream deterrents of Uty protection and are upregulated in PAH patient lungs in a sex-specific manner. (A) Comparison of RNA-sequencing (RNAseq) data from Si-Scrm and Si-Uty Hx mouse lungs revealed 523 differently expressed genes (DEGs) as represented by vertical columns on a heatmap depicting log fold change in expression. (B) Pathways enriched with DEGs include inflammation, cell signaling, extracellular matrix (ECM), transcription, and translation. (C) Integration of RNAseq data with an online microarray dataset of male and female human PAH lung samples revealed Cxcl9/CXCL9 and Cxcl10/CXCL10 as upregulated in PAH females (versus PAH males) and Si-Uty mice (versus Si-Scrm) as depicted in a heatmap representing individual patients’ relative gene expression. (D) Relative expression of CXCL9 and CXCL10 in human healthy and PAH lungs as measured by real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR). (E–G) Representative immunofluorescence staining of CXCL9 (E) and CXCL10 (G) in male and female lung tissue from healthy and diseased (PAH) patients. (F) Relative expression of CXCL9 and CXCL10 in human male and female PAH lungs as measured by real-time qPCR. Scale bars, 100 μm. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. Hx = hypoxia; KD = knockdown; WT = wild-type.
